|
|
Theoretical and Methodological Aspects of TranslationProblems for discussion: 1. Translation as a Notion, Subject and Object of Linguistic Study 2. Significance of Translation 3. Methods of Translation 4. Kinds of Translation
1. 1. Translation as a Notion and an Object of Linguistic Studies Translation can be seen from different points of view, as it can be a notion, a subject and an object of a linguistic study. The process of translation always involves two languages – a source language and a target language. A source language is an original language, the one from which the translation is done. A target language is a resulting language, the one into which the translation is done. As a notion translation means the process of rendering the content of a source language word, word-group, sentence or passage in the target language. Translation also denotes the result of the process of rendering. As a subject translation is a linguistic study which considers principles, methods and ways of conveying the meaning of a source language units in the target language. As an object of a linguistic study translation is functional interaction of two languages which involves extralinguistic situation and background information. Extralinguistic situation implies the conditions under which the communication takes place. Background information is general knowledge of the subject of communication. It is the translator’s common sense, his knowledge of the way the things are in life. According to its physicalparameters translation is divided into translation and interpretation. The difference between them is thattranslation is written while interpretation is oral. But it should be mentioned that the term ‘translation’ is much broader and it can be used when we speak about both translation and interpretation. Translation is divided into several types depending on the genre of the text being translated, such as literary, publicistic translation, translation of official documents, etc. Interpretationis traditionally divided into consecutive and simultaneous interpretation. Consecutive interpretation is the process of interpreting which follows the source utterance. Simultaneous interpretation is the process of interpreting performed at the same time with the original speech. As a rule, this interpretation requires special equipment, such as ear-phones, microphones and a sound- insulated booth.
Significance of Translation The importance of translation has long been recognized. It makes possible government and personal contacts at the international level. It is important for the functioning of different international bodies (E.E.C. –European Economic Council; I.M.F. – International Monetary Fund; UN, etc.). Translation is widely used in politics, business and science. Translation is a perfect means of sharing achievements and enriching national languages, literatures and cultures. Due to masterly translations of the world classics it has become part of many national literatures as well as the works of Ukrainian authors have become available for many readers abroad. Translation also promotes enrichment of lexicon in the target language (E.g. Cossack, steppe, hryvnia, etc.). A lot of expressions and regular sentence idioms have come to national languages owing to translation (E.g. Olympic calmness, the Ten Commandments, Trojan horse, to take part, time is money, black ingratitude, etc.). All this proves that the translator’s activities greatly influence the enrichment of languages through translation. 1. 2. Methods of Translation The main task of a translator is to make his translation as faithful as possible preserving the contents as well as the original manner and style of the author. There are some factors that predetermine the degree of faithfulness of translation which are as follows: 1. the purpose of the translation; 2. the skill of the translator/interpreter; 3. the type of the matter selected for translation. Depending on these factors there are the following methods of translation: 1. literal; 2. verbal; 3. word-for-word; 4. interlinear; 5. literary.
1. Literal translation is an equivalent rendering of the lexical meaning of each language unit despite the difference in the number of morphemes or syllables in the target language. It is used only at the word level. E.g. music-музик а, constitu tion -конститу ція, zoolog y -зоолог ія, atom ic -атом ний. 2. Verbal translation is conveying the additional meaning without rendering the orthographic or the sounding form of the source language units. It is the method of translation in which the lexical meanings in the source and the target languages are the same while the forms are different. Lexical meanings and morphological stems are identical in source and target languages. E.g. mis trust- не довіра, help less - без порадний, in correct- не правильний, super profit- над прибуток, weight lessness - не вагом іст ь. 3. Word-for-word translation is a consecutive verbal translation at the level of word-groups and sentences. This method is appropriate in rare cases as it is sure to lead to grammatical violations especially if the grammatical structures of the source and the target languages are different. E.g. He went to school.Він пішов до школи. Who said it? Хто сказав це? 4. Interlinear translation is a strictly faithful rendering of sense expressed by word-groups and sentences at the level of some text, which is normally achieved through many structural transformations. The necessity of these transformations is mostly explained by grammatical and stylistic differences in a source and target languages. E.g. He fell ill. Він захворів. Let’s discuss this problem to begin with. Давайте спочатку обговоримо цю проблему. 5. Literary translation is of two types: literary artistic and literary proper translation. Literary artistic translation is a faithful conveying of content and artistic merits of a fiction work. Literary proper translation is a faithful conveying of content of a non-fiction work. Literary translations are always performed with many transformations which help achieve the ease and beauty of the original composition Literary translation often requires linguistic and historical inquiries to clear up the obscure places. E.g. „Слово о полку Ігоревім”: word-for-word translation ‘A Word about Ihor’s Regiment’ Literary translation: The Tale of the Host of Ihor The Tale of the Armament of Igor Prince Igor’s Raid against the Polovtsi The Song of Igor’s Campaigne. Kinds of Translation Depending on the form of conveying the content the following kinds of translation are distinguished: 1. the written from a written matter translating; 2. the oral from an oral matter interpreting; 3. the oral from a written matter interpreting (at sight). Translation can also be descriptive and antonymic. Descriptive translation is conveying the sense of language units with their structural transformations in order to explain their meaning. It is often used in translating the notions of specific national lexicon. E.g. custard – заварний крем з фруктами verbal – неособова форма дієслова It is also rather often used in translating idioms. E.g. as mad as a hatter – зовсім божевільний all my eye and Betty Martin - нісенітниці like twelve o’clock – вмить, прожогом. Antonymic translation is a way of rendering positive in structure language units through negative in sense but identical in content language units or vice versa. E.g. Keep the door open. Не зачиняйте двері. I wish it were summer now.Шкода, що зараз не літо. I don’t think it will hurt you. Думаю, це вам не зашкодить.
SELF-ASSESSMENT TEST 1 1. Extralinguistic situation implies a) linguistic peculiarities of speech b) stylistic characteristics c) conditions under which communication takes place
2. Hierarchy of methods of translation is crowned with a) literary translation b) literal translation c) word-for-word translation
3.Literal translation is used at a) speech level b) word level c) language level
4. Verbal translation doesn't render a) lexical meaning b) orthographic from c) additional meaning
5. Literal translation always demonstrates coincidence of a) form and meaning b) form and connotation c) denotation and connotation
6. Interlinear translation is achieved through a) sound form b) orthographic form c) transformations
7. Descriptive translation is often used in rendering a) barbarisms b) internationalisms c) nationally biased units
8. In antonymic translation form and structure are a) the same b) different c) partially coincide
9. Consecutive translation takes place a) at the same time with a source utterance b) after the source utterance c) before the source utterance
10. Descriptive translation is conveying a) the sense of language units b) the form of language units c) the structure of language units
  Живите по правилу: МАЛО ЛИ ЧТО НА СВЕТЕ СУЩЕСТВУЕТ? Я неслучайно подчеркиваю, что место в голове ограничено, а информации вокруг много, и что ваше право... 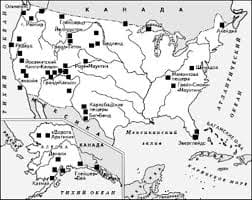 Система охраняемых территорий в США Изучение особо охраняемых природных территорий(ООПТ) США представляет особый интерес по многим причинам... 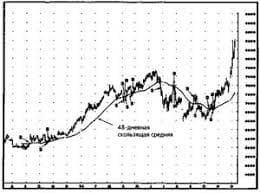 Что вызывает тренды на фондовых и товарных рынках Объяснение теории грузового поезда Первые 17 лет моих рыночных исследований сводились к попыткам вычислить, когда этот... 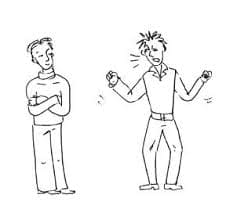 ЧТО ТАКОЕ УВЕРЕННОЕ ПОВЕДЕНИЕ В МЕЖЛИЧНОСТНЫХ ОТНОШЕНИЯХ? Исторически существует три основных модели различий, существующих между... Не нашли то, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском гугл на сайте:
|