|
|
The Subjective Participial Construction.This participial construction looks very much like the corresponding construction with the infinitive but it is used rather seldom. It is mostly found with the verbs denoting sense perception and the verbs of mental activity. With the verbs of sense perception we usually use Participle I which means that the noun or pronoun expressing the nominal part is the doer of the action. As a result the participle has an active meaning. On the contrary, with verbs denoting mental activity we usually find Participle II which shows that the noun or pronoun expressing the nominal part of the construction is not the doer but the object of the action. Consequently, the participle expresses a passive meaning. As a rule, the Subjective participial construction is translated into Ukrainian by an object clause preceded by an indefinite-personal sentence. In Ukrainian translation we usually use the conjunctions як, що. E.g. She was seen crossing the street early in the morning. Бачили, як вона переходила вулицю рано вранці. This mission is considered completed. Це завдання вважається завершеним. /Вважається, що це завдання завершене. 1. 4. The Nominative Absolute Participial Construction Its translation mostly depends on the syntactic function of this multifunctional construction. Generally it’s rendered by a subordinate or coordinate clause. If it is used as an adverbial modifier of time in Ukrainian translation the clause is introduced by the conjunctions КОЛИ, ПІСЛЯ ТОГО ЯК. E.g. The task completed he could have a rest. Коли справу було завершено, вони вирішили перепочити. As an adverbial modifier of cause this construction requires the conjunction ОСКІЛЬКИ. Sometimes the construction itself is not preceded by a conjunction though the clause which follows it is introduced by the conjunction А ТОМУ. E.g. It being very hot and stuffy he felt quite drained. Оскільки було дуже спекотно і задушливо, він почувався зовсім виснаженим. It being too late to catch a train he decided to wait. Було надто пізно, щоб встигнути на поїзд, а тому він вирішив зачекати. As an adverbial modifier of condition the construction is introduced by the conjunctions ЯКЩО, ЗА УМОВИ ЩО. E.g. The weather permitting, we can admire the beauty of this quiet nook. Якщо дозволить погода/погода не зіпсується, ми можемо помилуватися красою цього тихого куточка. As an adverbial modifier of attendant circumstances the construction is rendered by a coordinate clause introduced by the conjunctions І, А. Sometimes we can use a participial phrase (дієприслівниковий зворот). E.g. She looked at me her hands clasping nervously. Вона дивилася на мене, нервово стискаючи руки. / Вона дивилася на мене, а її руки нервово стискалися. 1. 5. The Prepositional Absolute Participial Construction This construction is monofunctional, as it can be used only as an adverbial modifier of attendant circumstances. In English it is always introduced by the preposition WITH. It’s important to mention that this preposition is very rarely translated into Ukrainian. E.g. She sat on the sofa with her head bent. Вона сиділа на дивані з опущеною головою. In most cases it is translated by a coordinate clause introduced by the conjunctions А,І as well as a participial phrase (дієприслівниковий зворот). This translation can be explained by the syntactic function of an adverbial modifier denoting an action which accompanies the action expressed in the main clause. E.g. She sat quietly with her eyes fixed on the fire. Вона спокійно сиділа, не зводячи очей з вогню. The girl rushed out of the room, her father following her. Дівчинка вибігла з кімнати, і батько прослідував за нею.
1. 6. The Nominative Absolute and the Prepositional Absolute Constructions These constructions structurally look very much the same as the corresponding participial constructions. The relation of the predication in complexes of this type is realized through a prepositional phrase, an adjective, or an adverb. Like in the above-mentioned constructions, their translation depends on their syntactic functions. The Nominative Absolute Construction usually performs the function of an adverbial modifier of time and it’s translated by a clause of time introduced by the Ukrainian conjunctions КОЛИ, ПІСЛЯ ТОГО ЯК. E.g. The children hungry, the mother gave them some sandwiches. Коли діти зголодніли, мати нагодувала їх бутербродами. In the function of an adverbial modifier of attendant circumstances both constructions are translated by participial phrases or coordinate clauses with the conjunctionsІ, А. E.g. She sat, her eyes on fire. Вона сиділа, не зводячи очей з вогню. Now, with this visit in prospect, he couldn’t think of anything else. Тепер, плануючи цю поїздку, він не міг думати ні про що інше. It’s important to remember about the peculiarities of translation of the Nominative Absolute Participial and Nominative Absolute Constructions which structurally look rather similar. In case there is the adverb OVER in them, their meaning and consequently the translation can be quite different. The Nominative Absolute Participial construction in which the adverb OVER is preceded by participle I of the verb TO BE, always has a causal meaning and the clause in Ukrainian translation is introduced by the conjunction ОСКІЛЬКИ. E.g. The classes being over, the children went home. Оскільки заняття закінчились, діти пішли додому. The Nominative Absolute Construction in which the adverb OVER follows the nominal part, expresses the temporal meaning and the clause is introduced by the conjunctions КОЛИ, ПІСЛЯ ТОГО ЯК. E.g. The classes over, the children went home. Коли заняття закінчилися, діти пішли додому. This difference in translation can be explained by the peculiarity of participle I of the verb TO BE which never expresses temporal meaning.
SELF-ASSESSMENT TEST 6 1. The number of participial constructions is a) 6 b) 4 c) 2
2. The verbal which is never used parenthetically is a) the gerund b) the infinitive c) Participle I
3. The verbal which has no tense and voice distinctions is a) Participle I b) Participle II c) the Gerund
4. Priority of the action can be expressed by Participle I Indefinite of verbs denoting a) compulsion and motion b) sense perception and motion c) sense perception and compulsion
5. The second part of constructions without participle can be expressed by a) an adjective, an adverb or a prepositional phrase b) a noun, an adverb or a prepositional phrase c) an adjective, an adverb or a participial l phrase
6. Which of the constructions is monofunctional? a) the Objective Prepositional Construction b) the Nominative Absolute Participial Construction c) the Nominative Absolute Construction 7. Which of the constructions is multifunctional? a) the Subjective Participial Construction b) the Prepositional Absolute Participial Construction c) the Nominative Absolute Construction 8. The participle can be used with a) conjunctions b) interjections c) prepositions
9. The participle combines a) nominal, adjectival and verbal characteristics b) adverbial, adjectival and verbal characteristics c) nominal, adjectival and nominal characteristics
10. The participle is never used as a simple object because it lacks a) verbal character b) adjectival character c) nominal character   Система охраняемых территорий в США Изучение особо охраняемых природных территорий(ООПТ) США представляет особый интерес по многим причинам... 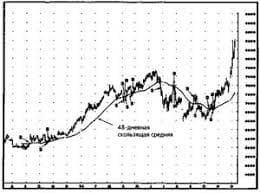 Что вызывает тренды на фондовых и товарных рынках Объяснение теории грузового поезда Первые 17 лет моих рыночных исследований сводились к попыткам вычислить, когда этот...  Что делать, если нет взаимности? А теперь спустимся с небес на землю. Приземлились? Продолжаем разговор...  ЧТО И КАК ПИСАЛИ О МОДЕ В ЖУРНАЛАХ НАЧАЛА XX ВЕКА Первый номер журнала «Аполлон» за 1909 г. начинался, по сути, с программного заявления редакции журнала... Не нашли то, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском гугл на сайте:
|