|
|
Digital Video Applications - User BenefitsVideo Conferencing Digital video makes it possible for businesses to enhance their capabilities to deliver more competitive products and services. Much of business is now conducted by phone, which is, by its nature, one dimensional and lacking in the ability to convey the subtleties of body language and other robust visual attributes such as a whiteboard. By having the ability to share a whiteboard over the phone makes it easier to convey ideas and graphic depictions. The solution is to combine voice/video/whiteboard so that phone-based discussions become more personal and more productive. No matter what cameras, compression techniques, and viewing devices you select, using either an ATM-based infrastructure or an IP/Ethernet edge with an ATM core will ensure that the video/audio/whiteboard will be transmitted error free even if there is other traffic on the same link. Video Archival and Retrieval VCR tapes are the most common vehicles for analog video archival. Typically, however, tapes must be inserted manually, which makes for a labor-intensive process. Also, VCR tapes jam periodically and have a limited shelf life. If digital video surveillance were used, your digital video would be able to travel uninterrupted from the camera source to a digital archival system, which would require little human intervention. This would be the same source that your security personal are watching. Marconi's ATM switches have the ability to efficiently make copies of data and send that data to multiple locations. This is known as multicasting. Your security personnel could be in one building while your archival system could be miles away. Distance Learning Distance learning is a natural use for Video Conferencing. Distance learning can be defined as any learning that takes place with the instructor and students are remote from each other in classroom environments or even to the home. Distance Learning has many benefits, including: - School district with limited resources to hire many Foreign Language Teachers. With the proper Video setup, that one teacher can teach classes in other schools within the school district. - Students who live in rural areas, who are not able to attend world-class universities can have high quality 2-way video with the use of ATM networking and Video Conferencing gear. Video Surveillance Airports and other vital facilities are under increasing scrutiny to increase their video surveillance activities to locate any suspicious activity. This has led to an increase in the number of cameras that they need to deploy, monitor and archive. Moving to a networked infrastructure, deployment of thousands of cameras is now more feasible and reliable. Video can be multicast to various locations so that an archiver can be digitally recording the same material as what is being viewed on monitors. Video Arraignment Large communities would like to have their police officers spend more time enforcing laws than waiting to see a judge after a criminal has been apprehended. By installing video conferencing gear, taxpayers will be able to save on the expense of transporting inmates to court is eliminated in many cases. Eliminating the possibility of escape during the transportation of inmates is one of the many benefits resulting from conducting video arraignments. Tele Medicine In the emerging realm of Telemedicine, digital video is making it possible to extend the best medical service to remote or underserved areas of the population. It also makes it possible to leverage the best medical expertise at multiple sites, quickly and efficiently, for collaborative and remote diagnosis, as well as evaluation of medical imagery such as X-rays and MRI images. Digital video provides an intangible "human touch" that is invaluable to cultivating and enhancing business relationships with customers, suppliers, partners and employees. Just as significantly, digital video can help business attain tangible benefits through cost savings, reduced capital expenditures, improved operational efficiencies, better communications and enhanced customer service. It is for these reasons that businesses will increasingly adopt networked digital video as a competitive asset. ~ 3568 Comments: a subtlety -острота, тонкость (понимания, анализа и т. п.); проницательность a whiteboard – виртуальная аудиторная доска, разделяемая виртуальная аудиторная доска, виртуальная "классная" доска, виртуальная лекционная доска, разделяемый блокнот. Используемое для видеоконференцсвязи программное средство в виде графического редактора растровых изображений, в котором участники конференцсвязи пишут или рисуют (как мелом на доске). to jam – заедать, застревать, заклинивать; останавливать(ся) (о машине и т. п.) a scrutiny -внимательный осмотр; исследование, наблюдение to deploy -использовать, употреблять; развертывать an arraignment -привлечение к суду; обвинение, предъявление обвинения X-rays – рентгеновы лучи MRI ( magnetic resonance imaging ) – магнитно-резонансное исследование Satellite Television Satellite television is television delivered by way of communications satellites, as compared to conventional terrestrial television and cable television. In many areas of the world satellite television services supplement older terrestrial signals, providing a wider range of channels and services, including subscription-only services. Satellites used for television signals are generally in either highly elliptical (with inclination of +/-63.4 degrees and orbital period of about 12 hours) or geostationary orbit 37,000 km (22,300 miles) above the earth’s equator. Satellite television, like other communications relayed by satellite, starts with a transmitting antenna located at an uplink facility. Uplink satellite dishes are very large, as much as 9 to 12 meters (30 to 40 feet) in diameter. The uplink dish is pointed toward a specific satellite and the uplinked signals are transmitted within a specific frequency range, the leg of the signal path from the satellite to the receiving Earth station is called the downlink. A typical satellite has up to 32 transponders for Ku-band and up to 24 for a C-band only satellite, or more for hybrid satellites. Typical transponders each have a bandwidth between 27MHz and 50MHz Each geo-stationary C-band satellite needs to be spaced 2 degrees from the next satellite (to avoid interference). For Ku the spacing can be 1 degree. This means that there is an upper limit of 360/2 = 180 geostationary C-band satellites and 360/1 = 360 geostationary Ku-band satellites. C-band transmission is susceptible to terrestrial interference while Ku-band transmission is affected by rain (as water is an excellent absorber of microwaves). The satellite receiver demodulates and converts the signals to the desired form (outputs for television, audio, data, etc.). Sometimes, the receiver includes the capability to unscramble or decrypt; the receiver is then called an integrated receiver/decoder or IRD. The cable connecting the receiver to the LNBF or LNB must be of the low loss type RG-6 or RG-10, etc. It cannot be standard RG-59. (A new form of omnidirectional satellite antenna, which does not use a directed parabolic dish and can be used on a mobile platform such as a vehicle, was recently announced by the University of Waterloo. Analog television distributed via satellite is usually sent scrambled or unscrambled in NTSC, PAL, or SECAM television broadcast standards. The analog signal is frequency modulated and is converted from an FM signal to what is referred to as baseband. This baseband comprises the video signal and the audio subcarrier(s). The audio subcarrier is further demodulated to provide a raw audio signal. There are three primary types of satellite television usage: reception direct by the viewer, reception by local television affiliates, or reception by headends for distribution across terrestrial cable systems. Direct to the viewer reception includes direct broadcast satellite or DBS and television receive-only or TVRO, both used for homes and businesses including hotels, etc.~2589
Comments: an inclination – отклонение, угол наклона a geostationary orbit -геостациона́рная орбита (ГСО) — круговая орбита, расположенная над экватором Земли (0° широты), находясь на которой, искусственный спутник обращается вокруг планеты с угловой скоростью, равной угловой скорости вращения Земли вокруг оси, и постоянно находится над одной и той же точкой на земной поверхности. an uplink -спутниковый канал связи a downlink -пересылка данных с искусственного спутника на наземную станцию a transponder -маяк-ответчик, ответчик, радиомаяк-ответчик Ku-band -Ku-диапазон — диапазон частот сантиметровых длин волн, используемых в спутниковом телевидении. C-band – С-диапазон - это оригинальная частота выделения для спутников связи. to unscramble – расшифровывать; syn. to decrypt -дешифрировать integrated receiver/decoder or IRD -интегральный приемник/декодер - электронное устройство, используемое для приема сигнала на радио частоте и преобразования цифровой информации, передаваемой ему. LNBF or LNB -low-noise block converter - cпутниковый конвертор или дословно малошумный конвертор-моноблок — приёмное устройство, объединяющее в себе предусилитель сигнала LNA (Low-Noise Amplifier), принимаемого со спутника, и понижающий конвертор (Downconverter) он же гетеродин (стабилизированный источник высокой частоты, вырабатывающий синусоидальный сигнал), служащего для преобразования частоты электромагнитной волны Ku или С-диапазона в промежуточную частоту от 950 до 2150 МГц, называемую L-диапазоном, с целью передачи с наименьшими потерями по коаксиальному кабелю до потребителя. RG-6 or RG-10 -телевизионный кабель (Broadband/Cable Television), 75 Ом. Кабель категории RG-6 имеет несколько разновидностей, которые характеризируют его тип и материал исполнения. RG-59 - телевизионный кабель (Broadband/Cable Television), 75 Ом. Российский аналог РК-75-х-х («радиочастотный кабель») omnidirectional - действующий по всем направлениям; не имеющий определенного направления действия; получающий и рассылающий радиоволны во все направления an affiliate -филиал, отделение SECAM - ( от фр. Séquentiel couleur avec mémoire, позднее Séquentiel couleur à mémoire — последовательный цвет с памятью. Система аналогового цветного телевидения, впервые применённая во Франции. Исторически она является первым европейским стандартом цветного телевидения. a subcarrier -поднесущая, субнесущий a headend - головной узел (в компьютерной сети)
  Что способствует осуществлению желаний? Стопроцентная, непоколебимая уверенность в своем...  ЧТО ТАКОЕ УВЕРЕННОЕ ПОВЕДЕНИЕ В МЕЖЛИЧНОСТНЫХ ОТНОШЕНИЯХ? Исторически существует три основных модели различий, существующих между...  ЧТО ПРОИСХОДИТ ВО ВЗРОСЛОЙ ЖИЗНИ? Если вы все еще «неправильно» связаны с матерью, вы избегаете отделения и независимого взрослого существования... 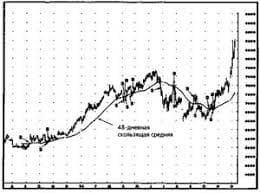 Что вызывает тренды на фондовых и товарных рынках Объяснение теории грузового поезда Первые 17 лет моих рыночных исследований сводились к попыткам вычислить, когда этот... Не нашли то, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском гугл на сайте:
|