|
|
Reproduce the context in which the following word-combinations are used.- common types - one-person business - an association of people - to take decisions - to be responsible for - to be liable for - to carry on business - to own and operate - benefit - profit
Vocabulary Focus 1. Complete the gaps choosing the right alternative. 1. In a partnership, the business is … by two or more people. a) varied b) assumed c) owned 2. Every job has its …. a) disadvantages b) enterprise c) tax 3. Demand for certain products … with the season. a) contributes b) flows in c) varies 4. Mr Lee … many charities. a) assumes risks of b) contributes to c) flows in 5. He packed all his … into one bag. a) possessions b) ownership c) liabilities 6. I didn’t get much … from this transaction. a) responsibility b) benefit c) disadvantage 7. The baker has … business here for years. a) varied b) carried on c) flown in
2. Look through the text once again and find the English equivalents. предоставлять товары и услуги несколько стандартных типов быть ответственным за успех или неудачу исключительное право на прибыль нести персональную ответственность за долги быть образованным с целью; с целью ведения бизнеса передача фондов агентские (посреднические) отношения коммерческий или некоммерческий контролировать потоки денег
3. Change the words on the right to complete the sentences below.
Talking points
1. The choice of the form of business or business organization depends on various factors. Share your ideas about them. 2. Partnerships consist of two or more partners who are both responsible for the business. They share assets, profits, liabilities, and management responsibilities for running the business. Before making a decision concerning whether to have a partner or not, it is better to prepare a "for" and "against" list. What are the most common reasons for joining with another person to start the business? Discuss all the advantages and disadvantages with your partner and make a "for" and "against" list. 3. In your opinion, do men or women make more successful business people? Why? Summary Points 1. Summarize the main idea of the text below. There are numerous reasons that make people think about owning a business of their own. Personal independence, unlimited profit potential, the opportunity to work at something they really love are some of the reasons people have given for trying entrepreneurship. Many business leaders begin their careers as entrepreneurs after four years of undergraduate college training and even additional graduate school training. Others become successful entrepreneurs without special training. Many colleges now offer programs that teach students how to start and operate a business. Basic information is combined with hands-on experience and the advice of successful business consultants. These programs help potential entrepreneurs decide whether their own ideas are good and how to follow through with them. A common way to learn about business, and the opportunities for starting one similar to it, is to learn while working for someone else. It provides a source of steady income to people while they are planning to start their own businesses. About 50 percent of entrepreneurs start their businesses in industries in which they have some experience.
2. Divide the text into logical parts and use appropriate vocabulary to make its summary. Unit 11 GOVERNMENT AND BUSINESS Lead-in Classify the tasks you consider to be governmental responsibilities in order of importance. - education - health care - working conditions - social security - defence - public transport
Key Vocabulary
Study the following list of vocabulary.
Pre-reading Activities Translate the sentences into Russian. Mind the list of Useful Vocabulary. 1. If inflation threatens the US economy, the Federal Reserve System may adopt policies that increase interest rates. 2. During a depression the government may try to increase demand by cutting taxes so that people have more money to spend. 3. An essential part of economic freedom is freedom to use the resources we possess in accordance with our own values. 4. In some countries producers don’t depend on the government regulations and make all decisions themselves. 5. A mixed type of economy with a rather high degree of government intervention is a feature of some developed countries, such as the USA, Canada, Japan. Reading
1. Read the text. Ask 4-5 questions about its contents and let the group answer them. To what extent should the government interfere in the economic system? On the one hand, it can intervene minimally, allowing the forces of supply and demand and the price mechanism to determine what goods and services are to be produced. On the other hand, the government can make all major decisions such as what to produce, how to produce and for whom to produce. Most governments operate between these two extremes. But there are always some things which are under the government’s control. For example, health care is a sphere of a state responsibility in all civilized lands, as no one can be assigned to illness or death because of poverty. The state has many other essential functions: parks and recreational facilities, the police, libraries and others. By the way, to support science is also the government’s responsibility. Together with this, it usually invests in agricultural productivity, modern air transport, advanced information technologies and the environment. The USA points to its free enterprise system as a model for other nations. But exactly how free is business in America’s free enterprise system? The answer is, not completely, because a complex web of government regulations shapes many aspects of business operations. It is known that historically, the US government policy toward business was summed up by the French term laissez-faire – “leave it alone”, but laissez-faire practices haven’t prevented private interests from turning to the government for help on numerous occasions, such as grants of land and public subsidies, protection against strong competition, tax breaks and others. As for the British government, it seeks to fine-tune the economy in order to keep economic booms from becoming too inflationary and recessions from becoming too deep. The British government often manages demand, intervening when demand for goods and services is high enough to threaten inflation. In such cases the government tries to reduce demand by raising interest rates and taxes. In economic emergencies the government can control prices and incomes to a considerable extent, but this is done only in extreme circumstances such as in times of war and runaway inflation.
Comprehension Check 1. Agree or disagree with these statements about the text. 1. Sports care is a sphere of state responsibility in all civilized lands. 2. China points to its free enterprise system as a model for other nations. 3. A complex web of the US government regulations shapes many aspects of business operations. 4. In economic emergencies the British government never controls prices and incomes.
2. Find the paragraph, which gives the answer to the following question. - What spheres of life are usually under the government control?
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3
3. Complete the sentences using the information from the text. 1. As for the British government, it seeks to ………. 2. The state has many other essential functions: ………. 3. On the other hand, the government can make ………. 5. In economic emergencies the government can ……….
Vocabulary Focus
1. Match the words on the left with their synonyms on the right. 1. essential a. decrease 2. interfere b. let 3. reduce c. important 5. allow e. regulate
2. Use the words from the list of Useful Vocabulary to complete the sentences. 1. The American ….. emphasizes private ownership. a. deep recession b. free enterprise system c. interest rate 2. While most Americans would agree that ….. has an important role to play in the economy, there is a considerable disagreement as to how active this role should be. a. government b. environment c. responsibility 3. People who ….. in education, gain profit in the form of knowledge. a. interfere b. invest c. reduce 4. A serious, long-lasting ….. is called a depression or a slump. a. inflation b. increase c. recession 5. In carrying out ….., the government uses a combination of monetary and fiscal policies. a. fine-tuning b. laissez-faire c. tax breaks 6. If a(n) ….. is lowered, businesses will borrow more from the banks, jobs will be created, but prices might rise and that means inflation. a. run-away inflation b. government regulation c. interest rate
3. Give the English equivalents to the following expressions. - чрезвычайное экономическое положение - налоговые льготы - безудержная инфляция - производить товары и услуги - современные информационные технологии - принимать решения - поднять процентную ставку - контролировать цены и доходы
Talking Points
1. Comment on the quotations. 1. “Which is the best government? That which teaches us to govern ourselves”. Johann Wolfgang von Goethe 2. “That government is the best which governs least, because its people discipline themselves”. Thomas Jefferson
2. Express your opinion on the following issues. 1. To what extent should the government interfere in the economic system? 2. Some economists state that the government interferes in the economy too much. Others say it should do more. What are your arguments for and against government control? While answering this question, you may use the following phrases. - To my mind ……… - I think ……… - In my opinion ……… - On the one hand ………, on the other hand ……… Summary Points 1. Read the text and choose the most suitable title out of those given below. A. Small Business in the USA. B. The Role of the Government and Individuals in the American Economy. C. The Mixed Type of the American Economy.
The American free enterprise system emphasizes private ownership. Private businesses produce most goods and services, and almost two thirds of the output goes to individuals for personal use. However, there are limits to free enterprise system. Americans have always believed that some services are better performed by public rather than private enterprises. For example, in the US the government is responsible for the administration of justice, education (although there are many private schools), road system, and national defense. The American government also provides unemployment benefits to people who cannot support themselves; it pays much of the cost of medical care for those who live in poverty; it regulates private industry to limit air and water pollution; it provides low-cost loans to people who suffer from natural disasters; and finally, it has played the leading role in the exploration of space, which is too expensive for any private enterprise to handle. In the American economic system, individuals can help guide the economy through the choices they make as consumers and through the votes they cast for officials who shape economic policy. In recent years, consumers have voiced concerns about product safety, environmental threats and potential health risks. The government, in its turn, has responded by creating agencies to protect consumer interests. The US economy has recently changed in other ways as well. The labor force has shifted to service industries. In today’s economy, there are much more providers of services than producers of agricultural and manufactured goods.
Notes: cast votes – голосовать voice concern – выражать беспокойство shift v– перемещать(ся), передвигать(ся)
2. Put down key words and expressions from each paragraph. 3. Summarize the text, basing on the key words and expressions you have put down. Unit 12 CORPORATE CULTURE Lead-in 1. Split into groups. Within your group discuss the issues below. Share the opinion of your group with the others. 1. How do you understand the term “corporate culture”? 2. What is the role of corporate culture in successful business?
2. Choose the factors which are influenced by corporate culture. Then comment on your choice. - communication in the company - profit of the company - planning - decision-making - image of the company - management of the company - size of the company - personal relations in the company - hobbies and interests of employees - payment of work in the company
Key Vocabulary
Study the following list of vocabulary.
Pre-reading Activities
1. Complete the table with missing words. Consult a list of Key Vocabulary and a dictionary if necessary.
2. Translate the sentences into Russian. Mind the words from exercise 1. 1. People’s creativity is restricted by routine and traditional office hours. 2. Many governments cut advertising expenditures during poor economic times. 3. A slogan is believed to express a key corporate value. 4. In recent years, there have been changes in employment, which have affected practically all the work force. 5. It’s known that employee’s behavior influences the image of the company. Reading
Read the text and be ready to speak about corporate culture and its characteristics.
Corporate culture can be defined as a set of key values, beliefs, understandings and norms shared by members of an organization. It represents the unwritten, informal norms that bind the company staff together. Just as tribal cultures have rules and taboos that dictate how members will act toward one another, modern organizations have cultures that govern how their members should behave. In every company, there are systems or patterns of values, symbols, rituals, myths, and practices that have evolved over time. These shared values determine what employees see and how they respond to their world. When confronted with a problem, corporate culture restricts what employees can do by suggesting the correct way – “the way we do things here” – to define, analyze and solve the problem. Corporate culture is a perception, because individuals perceive the culture of the company on the basis of what they see or hear within this company. Even though individuals may have different backgrounds or work at different levels in the organization, they tend to describe the organization’s culture in similar terms. That is the shared aspect of culture. Corporate culture is also a descriptive term, because it is concerned with how members perceive the company and it is not concerned with the fact whether they like it. So, corporate culture describes rather than evaluates. Research suggests that there are 7 characteristics which cover the essence of an organization’s culture. 1. Innovation and risk taking. The degree to which employees are encouraged to be innovative and to take risks. 2. Attention to detail. The degree to which employees are expected to show accuracy, analysis and attention to detail. 3. Outcome orientation. The degree to which managers focus on results or outcomes rather than on the techniques and processes used to achieve those outcomes. 4. People orientation. The degree to which management decisions take into consideration the effect of outcomes on people within the organization. 5. Team orientation. The degree to which work activities are organized around teams rather than individuals. 6. Aggressiveness. The degree to which people are aggressive and competitive rather than easygoing and cooperative. 7. Stability. The degree to which company activities emphasize maintaining the status quo in contrast to growth. Comprehension Check
1. Agree or disagree with these statements about the text. 1. Corporate culture represents the unwritten, informal norms that bind the company staff together. 2. Corporate culture evaluates rather than describes. 3. Research suggests that there are 10 characteristics which cover the essence of an organization’s culture. 4. In every company, there are systems or patterns of values, symbols, rituals, myths and practices that have evolved over time.
2. Answer the following questions. 1. How is corporate culture defined in the text? 2. Why is corporate culture considered to be a perception? 3. Why is corporate culture considered to be a descriptive term? 4. What are the characteristics which cover the essence of an organization’s culture?
3. Choose the suitable title for the first paragraph of the text. A. The shared values of corporate culture. B. The definition of corporate culture. C. The informal norms of corporate culture. Vocabulary Focus
1. Match the words with their definitions.
2. Use the words from the list of Useful Vocabulary to complete the sentences. 1. We use the term ….. to speak about a system of shared values that distinguish this organization from other ones. a. corporate culture b. background c. status quo 2. ….. are required to follow rules and regulations in this firm. a. researchers b. governments c. employees 3. They have their own interest in maintaining the …... a. accuracy b. perception c. status quo 4. She joined the ….. as an accountant. a. corporate culture b. staff c. research 5. Nothing will change my ….. in a promising future of our company. a. believe b. belief c. perceive 6. Mr. Black has the right ….. for this position. a. background b. perception c. behavior
3. Give the English equivalents to the following expressions. - система ценностей - решить проблему - иметь разное происхождение - сущность корпоративной культуры - быть конкурентоспособным - поддерживать статус-кво
Talking Points 1. Give your arguments for or against the following statements. 1. Corporate culture is especially important for top managers. 2. Corporate culture helps to improve quality management (управление качеством). 3. It’s impossible to change an organization’s culture.
2. Imagine you have got your own company. Describe an effective corporate culture you would like to have in it.
3. Finish the phrase. - A strong corporate culture helps …...
Summary Points 1. Read the passage and divide it into 3 paragraphs. Although all organizations have their own cultures, not all cultures have an equal influence on employees. Organizations where the key values are widely shared have strong cultures. The more employees accept the organization’s key values, the stronger the culture is. Employees in firms with strong cultures are more committed to their firms than employees in firms with weak cultures. Moreover, strong cultures are associated with high performance of organizations. Whether an organization’s culture is strong, weak, or somewhere in between, depends on the intensity with which the culture was originated. It is necessary to remember that organizations where the key values are intensely held and widely shared have strong corporate cultures.
2. Choose from the list A-D the sentence which best summarizes each paragraph (1-3) of the passage. There is one extra sentence which you don’t need to use. A. The main characteristics of strong cultures are: shared key values, employees’ commitment to their firm and high performance of the organization. B. Any organization has its own corporate culture. C. The cultures of some organizations encourage employees to take risks. D. The intensity with which the culture was originated plays the most important role.
3. Summarize the passage, basing on the sentences from Task 2. Unit 13 EMPLOYMENT Lead-in 1. In your opinion, which factors below are important for getting a job? Choose the five most important. Is there anything missing from the list? - age - appearance - contacts and connections - experience - handwriting - hobbies - marital status - qualifications - references - blood group - personality
2. Share your thoughts with the whole group on the following points.
1. Is employment a social issue or a political one? Explain your choice. 2. Do you believe that obtaining a good job today is easier or more difficult than in your parents’ day? Why?
Key Vocabulary
Study the following list of vocabulary.
Pre-reading Activities Translate the sentences into Russian. Mind the list of Useful Vocabulary. 1. My employer is a very generous person; he gives us all a big present at Christmas. 2. If you wish me to attend an interview, I am available at any time. 3. My new job requires a lot of skills in the IT sphere. 4. Our boss invited us to participate in a job-sharing scheme. 5. The work of a software developer can be tiring, but it demands a lot of creativity and brings a lot of satisfaction and positive emotions. 6. Many professional persons get a large amount of job satisfaction and a high income. Reading
1. Read the text and focus on types of employment and the main reasons for working. When we speak about employment we usually mean paid work done by a person or a group of people. There are different types of employment nowadays. The main goal of economy is full employment, which means availability of jobs for all employable citizens. Nowadays a lot of people work part-time; they perform their professional duties during a part of the regular working time. There has been a huge rise in part-time jobs of all kinds, ranging from the unskilled office cleaners to the highly skilled computer consultants. There is also job sharing. This is a practice of dividing a full time job between two people so that each works for half the time. We can also mention informal employment, or paid work on a casual basis. Jobs are often irregular, and workers are self-employed without earning pensions and without paying taxes. This sort of employment is common in urban areas of developing countries. It may involve service jobs as well as craft industries. With technological advances more and more people telework. It means working away from the employer’s office, often at home, but maintaining close contact with coworkers and managers using computers and IT. In some situations teleworking can increase an employee’s productivity; it also decreases the time they spend driving to and from work and at the same time decreases pollution from cars. But some managers feel uncomfortable with the lack of direct supervision they have over their teleworking employees, and some employees may dislike teleworking because of isolation from coworkers. But why do people work? This question is important for business. The management of any business must try to understand why people work and provide the right motivation to make them work more effectively. Of course, one of the main reasons for working is money. People work to get enough money to satisfy their basic needs. But money isn’t the only motivation. Belonging to a group is also a strong motivation for working people. A sense of security is another human need for most people, that is why employers try to provide different pension and sick-pay schemes. One more strong motivation for people is a sense of self-importance. To work efficiently, people want to feel their importance and necessity. Only in this case they will have job satisfaction – a sense that you are doing something you really want to do using all your skills and creativity. Comprehension Check 1. Agree or disagree with these statements about the text. 1. There is one type of employment nowadays. 2. The main goal of economy is full employment. 3. Nowadays a lot of people perform their professional duties during a part of the regular working time. 4. Job-sharing is a practice of dividing a full time job between two people so that each works for half the time. 5. With technological advances few people telework. 6. Money is not one of the main reasons for working.
2. Choose the answer (A, B or C) which you think fits best according to the text. 1. How many types of employment are mentioned in the text? A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 2. What reasons for working are mentioned in the text? A. money, belonging to a group, a sense of security, a sense of self-importance B. money, belonging to a group, a sense of winning, a sense of development C. money, a sense of satisfaction, happiness, creativity
3. Complete the sentences using the information from the text. 1. Full employment means …... 2. Job-sharing is a practice of …... 3. The management of any business must try to understand …... 4. People work to get enough money to …... 5. Job satisfaction is a sense that …...
Vocabulary Focus 1. Match the words on the left with those on the right. Then translate the expressions into Russian.
2. Use the words from the list of Useful Vocabulary to complete the sentences. 1. He is ….., that’s why he only goes to the office one day a week. a. teleworking b. coworker c. creative 2. One of the most difficult decisions is choosing what to do for a …... a. living b. work c. satisfaction 3. Most people are much more creative than their ….. realize. a. skills b. employers c. jobs 4. When she is 55, she will be able to give up work and live on her …... a. creativity b. employment c. pension 5. Sick-pay and pension schemes are the basic things which provide employees with a …... a. sense of responsibility b. sense of security c. sense of self-importance
3. Give the English equivalents to the following expressions. - работа на нерегулярной основе - профессиональные обязанности - типы занятости - платить налоги - городская местность - развитые страны - увеличить производительность - руководство предприятия - работать эффективно - удовлетворять нужды
Talking Points
1. Comment on the quotations. 1. It doesn’t matter what job you do. It matters how you do it. 2. I would rather be a happy dustman than an unhappy millionaire.
2. Which of the following is (was) the most important to you when deciding on a career? Rank the points, then discuss it with your groupmates. - long-term career prospects - personal satisfaction - good payment - opportunity to travel - using your initiative - chance to meet a lot of people
3. In pairs, discuss the following questions. 1. Are you sure /unsure about your career path? Why? 2. Are you optimistic/pessimistic about your prospects? Why? 3. Do you want to be self-employed or work as an employee? Why?
Summary Points 1. Read the text and choose the most suitable headline out of those given below. A. Importance of Job Interviews. B. Problems at Job Interviews. C. Basic Types of Job Interviews. D. Psychological Aspect of Job Interviews.
Job interviews can generally be divided into 3 main types. The first is called the “traditional interview”. This is usually a series of standard questions about qualifications, work experience, knowledge and expectations. Here you have a list of quite traditional questions, like “What duties did you have in your previous job?” This is still the model for a lot of interviews today. Then there is the “case interview” which is very challenging. Here the interviewer presents a problem and then asks questions to find out how the candidate would solve the problem. The “case interview” puts candidates in a pretty uncomfortable position because they are asked to do different things – to demonstrate that they can analyze the problem logically, and communicate effectively with the interviewer. The third type is known as the “behavioural interview”. Its task is to find out how candidates behave in certain situations. A typical question here may be “Can you give me an example of a situation where you had to follow orders that you didn’t agree with?” The answers to such questions disclose a lot of information and the interviewer can see more of the interviewee.
2. Put down key words and expressions from each paragraph. 3. Summarize the text, basing on the key words and expressions you have put down. Unit 14 GLOBALIZATION Lead-in 1. Choose the variant which best defines the word “globalization”. Then explain your choice. A. the process of exchanging information, ideas or feelings B. the process enabling financial and investment markets to operate internationally, largely as a result of deregulation and improved communication C. the process enabling people to cut their expenses and economize
2. Divide into 2 groups. Try to find some advantages and disadvantages of globalization. Then exchange your ideas.
Key Vocabulary
Study the following list of vocabulary.
Pre-reading Activities Translate the sentences into Russian. Mind the list of Useful Vocabulary. 1. Consortium is a group of companies in similar businesses working together. 2. Some people believe that free trade between nations can offer prosperity and growth for all countries and businesses. 3. India is the world’s major exporter of IT services. 4. Many economists from developed countries believe that globalization may be the explanation for key trends in the world economy. 5. Those who support anti-globalists say that globalization provokes cross-cultural problems in the world. Reading Read the following text and answer the questions that follow it. Globalization is a word which has existed since the 1960s and it is on everyone’s lips these days from politicians to businessmen. The term “globalization” is used to describe certain processes in the world today. Globalization is defined as the process enabling financial and investment markets to operate internationally, largely as a result of deregulation and improved communication. The accelerating pace of globalization is having a profound effect on life both in rich and in poor countries. Of course, many governments and businesses see a lot of advantages in the process of globalization. They believe that increasing free trade between nations will offer prosperity and growth for all countries and businesses. Globalization, they state, has already brought many benefits: global food production has risen steadily over the last years and malnutrition rates have fallen accordingly; citizens in less-developed countries have access to health care which is often supplied by foreign businesses. For companies globalization means increasing the number of countries of operation. For example, British Petroleum (BP) is probably the most global company in the world. It is interesting to see that in the USA its nationality has begun to disappear. Almost everybody in the US says BP, and not British Petroleum. It’s a local kind of company. So, for its supporters, globalization offers an opportunity rather than a threat. The leaders of the world’s major economies and big businesses are committed to protecting and promoting global commerce and trade. They believe that the world is moving towards an era of global markets and global companies. Together with this, anti-globalists emphasize that globalization threatens the environment as well as national cultures – they predict that it will make the rich nations richer and the developing countries poorer. Among other disadvantages of globalization there are such points as: - It can lead to big employment problems. - It lowers people’s living standards. - It prevents governments from controlling their welfare systems. - It creates cross-cultural problems between the East and the West. As we can judge, nowadays globalization is a controversial issue for businesses and governments all over the world. But it goes without saying that it’s also an important issue for the 21st century, which will continue to be the subject of debate among those who oppose, support or simply observe it. Comprehension Check
1. Answer the following questions. 1. How is globalization defined in the text? 2. What advantages do businesses and governments see in the process of globalization? 3. What disadvantages do anti-globalists emphasize? 4. What other disadvantages of globalization are mentioned in the text?
2. Complete the sentences using the information from the text. 1. For companies globalization means …... 2. For its supporters globalization offers …... 3. The term “globalization” is used to describe …... 4. The world is moving towards an era …... 5. Globalization prevents governments from …...
3. Summarize all the advantages and disadvantages of globalization given in the text. Can you add any others?
Vocabulary Focus
1. Match the words with their definitions.
2. Use the words from the list of Useful Vocabulary to complete the sentences. 1. As a result of ….. many businesses trade throughout the world. a. malnutrition b. globalization c. promotion 2. Governments are planning to expand the global economy by …..trade and economic interdependence. a. promoting b. fighting c. economizing 3. International furniture retailer IKEA announced that it will ….. the world’s ancient forests. a. trade b. supply c. protect 4. Cheaper housing would improve the ….. of ordinary people. a. living advantages b. living disadvantages c. living standards 5. The police have made no attempt to solve these …... a. standards b. issues c. businesses 6. The supporters of globalization state that it will lead the world to economic …... a. trade b. prosperity c. opportunity
3. Give the English equivalents to the following expressions. - угрожать окружающей среде - продвигать торговлю - финансовые и инвестиционные рынки - видеть много преимуществ - иностранное предприятие - создавать межкультурные проблемы
Talking Points
1. Comment on the quotations. 1. “It has been said that arguing against globalization is like arguing against the law of gravity”. Kofi Annan 2. “Globalization is a fact of economic life”. Carlos Salinas de Gortari
2. Express your opinion on the following points. 1. Globalization: is it good or bad? Why? 2. What is your opinion about the future of the process of globalization?
3. Finish the phrase. - I would (not) like to live in the era of globalization, because …...
Summary Points 1. Look through the text from Reading and fill in the missing parts of its plan. I. The definition of globalization. II. III. The disadvantages of globalization. IV.
2. Put down key words for each point of the plan. 3. Summarize the text, basing on the key words you have put down. Unit 15 THE FIRST MODERN ECONOMISTS Lead-in
1. Can you name any well-known economists? What were they famous for? 2. Who got the epithet «the father of economics»?
Key Vocabulary
1. Study the following list of vocabulary.
2. Mind the following common nouns. 1. mercantilist n - меркантилист (сторонник меркантилизма, системы взглядов на вопросы экономической политики, господствовавшей в 16 – 18 вв.) 2. physiocrat n - физиократ (представитель французской школы политической экономики в 18 веке)
Pre-Reading Activities 1. Use a dictionary and match the synonyms. Mind the use of the prepositions.
Reading
Read the text and assimilate its information. Between the 16th and 18th centuries the major countries of Europe believed in the economic theory of mercantilism. Mercantilists claimed that nations should behave as if they were merchants competing with one another for profit and like merchants, nations should protect business and industry. But for a group of 18th-centuary French philosophers and economists, the suggestion that nations should protect their own business and industry made no sense at all. Those were the physiocrats. They claimed that the products of agriculture and other natural resources were the true source of wealth. In other words, since real wealth came from the land, it followed that the best thing the government could do would be to keep its hands off business and let nature take its course. This idea was expressed in the slogan «laissez faire», (let people do as they choose).
The heart of Smith’s economic philosophy was his belief that the economy would work best without any government regulation. In this case, self-interest would lead companies to produce only those products that consumers wanted, and to produce them at the lowest possible cost. They would do this to outperform their competitors and gain the greatest profit. He believed that self- interest would benefit the society as a whole by providing it with more and better goods and services at the lowest prices. To explain why the society benefits when the economy is free of regulation, Adam Smith used the term «invisible hand», meaning the economic forces that today are called supply and demand. In his work «The Wealth of Nations» Adam Smith sounds realistic and practical, respectful of the classical past but at the same time dedicated to the great discovery of his epoch – progress. Although he was writing for his generation, his thoughts and ideas have always attracted the attention of all economists, that is why Adam Smith has remained a significant figure in the history of economic thought for more than 2 centuries.
Comprehension Check
1. Complete the following sentences. 1. The economic theory of mercantilism …. 2. Some French philosophers and economists claimed that …. 3. … in 1776. 4. A. Smith objected to …. 5. According to Smith, …. 6. Adam Smith used the term «invisible hand» to ….
2. Answer the questions. 1. What was the difference between mercantilists’ and physiocrats’ views? 2. What idea was expressed in the slogan «laissez faire»? 3. Why did the year of 1776 become very significant for the development of the world economic thought? 4. Who is considered to be the father of economics? 5. What theories formed the core of Smith’s philosophy? 6. Why has Adam Smith remained a significant figure in the history of economic thought?
3. Read the text once more and explain the meaning of the phrases below.
Vocabulary Focus
1. Provide appropriate English equivalents of the following collocations. - бороться (конкурировать) за прибыль - поддерживать промышленность - природные ресурсы - источник состояния - правительственное регулирование - производить те товары, которые нужны потребителям - превзойти конкурентов - предоставлять товары и услуги по самым низким ценам - история экономических учений.
2. Fill in the prepositions, if necessary. Translate the sentences into Russian. 1. Free market system allows businesses to compete … profit with a minimum of government interference. A) for b) with c) on 2. There are several reasons why I object … joining you. A) with b) to c) - 3. The production of this equipment depends … demand. A) in b) on c) at 4. Our company can provide goods or services … a low cost. A) at b) on c) of 5. You will gain … no profit by resistance. A) by b) in c) -
3. Use the vocabulary of the text to complete these sentences.
1. An individual who buys products or services for personal use and not for manufacture or resale is … a) a consumer b) a merchant c) an exporter 2. In economics, … is the amount of goods and services by a firm, industry, or country. a) trade b) output c) profit 3. A fundamental economic concept that describes the total amount of a specific good or service that is available to consumers is … a) demand b) supply c) a law 4. Adam Smith saw the creation of … as the combination of materials, labor, land, and technology in such a way as to gain profit. a) costs b) society c) wealth 5. The Peugeot engine has … its competitors this season. a) competed b) benefited c) outperformed 6. I didn’t want to … him or his company. a) rival b) compete c) produce Talking Points
1. Economic thought may be roughly divided into three phases: · Premodern (Greek, Roman, Arab); · Early modern (mercantilists, physiocrats); · Modern (since Adam Smith in the late 18th century). What new facts have you learnt about it from the text? Can you add anything else? 2. Comment on the quotation. “Labor was the first price, the original purchase - money that was paid for all things. It was not by gold or by silver, but by labor, that all wealth of the world was originally purchased.” Adam Smith. Summary Points
1. What is the basic topic of the text about first economists? 2. Draw up an outline of the text and give a one-sentence summary of each point. 3. Add some important information and make a conclusion: What have you learned from the text? Have you found it informative/ helpful/ interesting?
SUPPLEMENTARY READING Unit 1 Economics as a Science
The Business Cycle
The business cycle or trade cycle is a permanent feature of market economies: gross domestic product (GDP) fluctuates as booms and recessions succeed each other. During a boom, an economy (or at least part of it) expands to the point where it’s working at full capacity, so that production, employment, prices, profits, investment and interest rates tend to rise. During a recession, the demand for goods and services declines and the economy begins to work at below its potential. Investment, output, employment, profits, commodity, share prices and interest rates generally fall. A serious, long-lasting recession is called a depression or a slump. The highest point on the business cycle is called a peak, which is followed by a downturn or a period of contraction. Economists sometimes describe contraction as “negative growth”. The lowest point on the business cycle is called a trough, which is followed by a recovery or an upturn or a period of expansion. There are various theories as to th   Живите по правилу: МАЛО ЛИ ЧТО НА СВЕТЕ СУЩЕСТВУЕТ? Я неслучайно подчеркиваю, что место в голове ограничено, а информации вокруг много, и что ваше право... 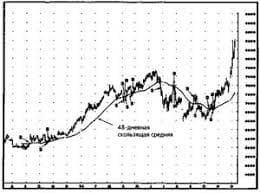 Что вызывает тренды на фондовых и товарных рынках Объяснение теории грузового поезда Первые 17 лет моих рыночных исследований сводились к попыткам вычислить, когда этот...  Что способствует осуществлению желаний? Стопроцентная, непоколебимая уверенность в своем...  ЧТО ПРОИСХОДИТ, КОГДА МЫ ССОРИМСЯ Не понимая различий, существующих между мужчинами и женщинами, очень легко довести дело до ссоры... Не нашли то, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском гугл на сайте:
|