|
|
УПРАВЛЕНИЕ ПРИ ЧРЕЗВЫЧАЙНЫХ СИТУАЦИЯХ
Теоретическая часть Данный лексический материал предназначен для того, чтобы студенты смогли составить высказывание о том, чем им придется заниматься, какова сущность дисциплины «Управление при чрезвычайных ситуациях» и с какими составляющими им придется иметь дело в данной области. emergency management управление при чрезвычайных ситуациях to avoid избегать, остерегаться disaster бедствие emergency evacuation аварийная эвакуация, эвакуация при чрезвычайных ситуациях quarantine карантин mass decontamination массовая дезинфекция, обеззараживание to rebuild восстановить, реконструировать human-made искусственного происхождения, антропогенный hazard риск, опасность to ameliorate улучшать responsibility ответственность (за что-л.) conventional structure традиционная, условная структура to exhaust исчерпывать, израсходовать mitigation смягчение, уменьшение preparedness подготовленность, готовность continuity целостность, связность dimension величина, степень, мера incident случай; происшествие military военный civil protection гражданская защита, гражданская оборона superintendent глава, директор, начальник, руководитель comprehensive всесторонний, полный preventive and preparatory measures предупреждающие и подготовительные меры disaster-resilient устойчивый, гибкий к бедствию risk-driven приводящий к риску integrated комплексный; единый collaborative общий, объединенный to facilitate облегчать; содействовать a common purpose общая цель
Задания Задание 1. Прочитайте и переведите текст:
EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT
Emergency management is the discipline of dealing with and avoiding risks. It is a discipline that involves preparing for disaster before it occurs, disaster response (e.g., emergency evacuation, quarantine, mass decontamination, etc.), and supporting, and rebuilding society after natural or human-made disasters have occurred. In general, any Emergency management is the continuous process by which all individuals, groups, and communities manage hazards in an effort to avoid or ameliorate the impact of disasters resulting from the hazards. Actions taken depend in part on perceptions of risk of those exposed. Effective emergency management relies on thorough integration of emergency plans at all levels of government and non-government involvement. Activities at each level (individual, group, community) affect the other levels. It is common to place the responsibility for governmental emergency management with the institutions for civil defense or within the conventional structure of the emergency services. However, emergency management actually starts at the lowest level and only increases to the next higher organizational level after the current level’s resources have been exhausted. In the private sector, emergency management is sometimes referred to as business continuity planning. Emergency Management is one of a number of terms which, since the end of the Cold War, have largely replaced Civil defense, whose original focus was protecting civilians from military attack. Modern thinking focuses on a more general intent to protect the civilian population in times of peace as well as in times of war. Another current term, Civil Protection is widely used within the European Union and refers to government-approved systems and resources whose task is to protect the civilian population, primarily in the event of natural and human-made disasters. Within EU countries the term Crisis Management emphasizes the political and security dimension rather than measures to satisfy the immediate needs of the civilian population. An academic trend is towards using the term disaster risk reduction, particularly for emergency management in a development management context. This focuses on the mitigation and preparedness aspects of the emergency cycle. Emergency managers are trained in a wide variety of disciplines that support them through out the emergency life-cycle. Professional emergency managers can focus on government and community preparedness (Continuity of Operations/Continuity of Government Planning), or private business preparedness (Business Continuity Management Planning). Training is provided by local, state, federal and private organizations and ranges from public information and media relations to high-level incident command and tactical skills such as studying a terrorist bombing site or controlling an emergency scene. In the past, the field of emergency management has been populated mostly by people with a military or first responder background. Currently, the population in the field has become more diverse, with many experts coming from a variety of backgrounds without military or first responder history. Educational opportunities are increasing for those seeking undergraduate and graduate degrees in emergency management or a related field. In 2007, Dr. Wayne Blanchard of FEMA’s Emergency Management Higher Education Project, at the direction of Dr. Cortez Lawrence, Superintendent of FEMA’s Emergency Management Institute, convened a working group of emergency management practitioners and academics to consider principles of emergency management. This project was prompted by the realization that while numerous books, articles and papers referred to “principles of emergency management,” nowhere in the vast array of literature on the subject was there an agreed-upon definition of what these principles were. The group agreed on eight principles that will be used to guide the development of a doctrine of emergency management. The summary provided below lists these eight principles and provides a brief description of each. Principles: Emergency management must be: 1. Comprehensive – emergency managers consider and take into account all hazards, all phases, all stakeholders and all impacts relevant to disasters. 2. Progressive – emergency managers anticipate future disasters and take preventive and preparatory measures to build disaster-resistant and disaster-resilient communities. 3. Risk-driven – emergency managers use sound risk management principles (hazard identification, risk analysis, and impact analysis) in assigning priorities and resources. 4. Integrated – emergency managers ensure unity of effort among all levels of government and all elements of a community. 5. Collaborative – emergency managers create and sustain broad and sincere relationships among individuals and organizations to encourage trust, advocate a team atmosphere, build consensus, and facilitate communication. 6. Coordinated – emergency managers synchronize the activities of all relevant stakeholders to achieve a common purpose. 7. Flexible – emergency managers use creative and innovative approaches in solving disaster challenges. 8. Professional – emergency managers value a science and knowledge-based approach; based on education, training, experience, ethical practice, public stewardship and continuous improvement.
Задание 2. Ответьте на вопросы: 1. What does Emergency Management deal with? What does it involve? 2. What does an effective emergency rely on? 3. What does modern thinking of Civil Protection focus on? 4. What is the characteristic feature of the EU Crisis Management? 5. What disciplines are emergency protectors trained in? 6. Are emergency protectors mostly with a military background? 7. What are the main principles to guide the development of a doctrine of emergency management? Задание 3. Переведите следующие словосочетания: Emergency evacuation, mass decontamination, integration of emergency plans, emergency services, private sector, business continuity planning, military attacks, government-approved systems, political and security dimensions, immediate needs, federal and private organizations. Задание 4. Переведите текст письменно и расположите абзацы текста в логико-хронологической последовательности: – 52 terminals, including 2 mobile ones of the All-Russian Complex System of Informing the Population were used to inform the population about the current situation. 5 informational messages containing the “hot-line” telephones, hospital addresses and medical institutions for children, bus routes, reoperated traffic along Sokolnicheskaya subway line were displayed. The information was also given through mass media (TV and radio channels, Information Agencies Websites). – At 08.36 Moscow time, the second explosion of the unknown model explosive device occurred in the third carriage of the electric train №45 at the “Park Kultury” subway station, following the route “South-Western” station – “Podbelskogo Str.” station. As a result of 2 explosions 134 people suffered, of whom 39 perished, 78 people were hospitalized to the medical institutions of Moscow. – At 18.00 the additional ground transportation finished its work. – Central Internal Affairs Directorate in Moscow organized the cordoning of the subway stations and nearby territories, traffic management. The train traffic was closed from the subway station “Komsomolskaya” till “Sportivnaya”. Additional trains were launched from “Belorusskaya” to “Tsaritsino” stations with the 20 minute interval. 131 busses were given by the “Mosgortrans” to arrange the traffic from the “Sportivnaya” to “Komsomolskaya” stations; traffic movement along the Garden Ring-road was arranged with a shorter period. – At 07.57 Moscow time on 29 March 2010, an explosion of the unknown model explosive device occurred in the 2nd carriage of the electric train №54 which was following the route “Podbelskogo Str.” – “South-Western”. – Operational groups EMERCOM of Russia, FSB of Russia and MIA of Russia were working at the site. – The specialists of the State Unitary Enterprise “Moscow Subway” together with the EMERCOM of Russia units evacuated 3500 people from the subway stations. – The psychologists of the Center of Emergency Psychological Aid EMERCOM of Russia (25 people) were working at the emergency site. 108 people received psychological aid and information-psychological support was rendered in 222 cases. – At 17.50, the traffic along the Sokolnicheskaya subway line was completely reoperated. – The psychologists of the Center of Emergency Psychological Aid EMERCOM of Russia were working at the site of the accident: at the “Lubyanka” station from 9.00 till 14.00 (4 people), at the “Park Kultury” station from 9.43 till 11.15 (4 people), at present 3 people are working in the mortuary №2 and 3 people are working in the mortuary №4.
Задание 5. Заполните пропуски предлогами: 1. Actions taken depend … part … perceptions … risk … those exposed. 2. It is common to place the responsibility … governmental emergency management … the institutions... civil defense or … the conventional structure … the emergency services. 3. Currently, the population … the field has become more diverse, … many experts coming … a variety … backgrounds … military or first responder history.
Задание 6. Составьте пять предложений из предложенных слов и словосочетаний: 1. Training/ local, state, federal and private/ is provided by/ organizations. 2. In the past/ emergency management/ by people/ with a military/ mostly/ or first responder background/ has been populated/ the field of. 3. Civil Protection/ and refers to government-approved systems/ within the European Union/ and resources/ is widely used. 4. In the private sector/ is sometimes referred to/ emergency management/ as business continuity planning. 5. Emergency management/ and avoiding risks/ dealing with/ is the discipline of.
Задание 7. Передайте основное содержание текста из задания 3.
Вопросы к практическому занятию 1. Что включает в себя дисциплина управления чрезвычайными ситуациями? 2. Какие существуют уровни управления чрезвычайными ситуациями? 3. Как осуществляется обучение специалистов управлению чрезвычайными ситуациями? Практическое занятие №   ЧТО ПРОИСХОДИТ, КОГДА МЫ ССОРИМСЯ Не понимая различий, существующих между мужчинами и женщинами, очень легко довести дело до ссоры... 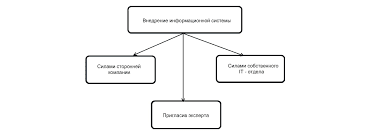 Что делает отдел по эксплуатации и сопровождению ИС? Отвечает за сохранность данных (расписания копирования, копирование и пр.)... 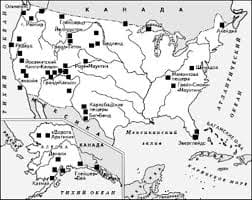 Система охраняемых территорий в США Изучение особо охраняемых природных территорий(ООПТ) США представляет особый интерес по многим причинам... 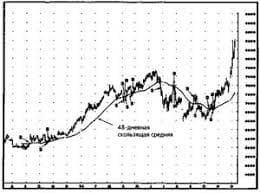 Что вызывает тренды на фондовых и товарных рынках Объяснение теории грузового поезда Первые 17 лет моих рыночных исследований сводились к попыткам вычислить, когда этот... Не нашли то, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском гугл на сайте:
|