|
|
Topic - 11. The doctrine of microevolution.Abstracts. 1. The concept of microevolution. Variability. Hereditary variability. Modification variability in the process of evolution. The concept of microevolution. The doctrine of microevolution - the central section of the modern theory of evolution - considering the mechanism of the evolutionary process, and includes chapters on the various factors of evolution, evolutionary material and evolutionary phenomena finally understood speciation and the emergence of various adaptation as the main result of the evolutionary process at this level. Rigorous analysis in any area is possible only when it is possible to isolate and describe the basic structural units and the processes occurring in them. He made reference to microevolutionary events through the use of the ideas and approaches of genetics. Microevolution examines the factors and mechanisms of intraspecific differentiation, ending speciation. It is here that the mechanism is implemented with all grandioznogo evolutionary process on Earth. In classical Darwinism initial stages of speciation remained unexplored, they just make up the foundations of the modern theory of microevolution. Variability. Variability is called a general property of organisms acquire new features, differences between individuals within a species. Variability of all the signs of organisms: the external and internal features of the structure, physiology, behavior, and others. In the progeny of a single pair of animals or plants grown from seeds per fruit, it is impossible to meet exactly the same individuals. In a herd of sheep of the same breed, each animal is different faint features: body size, long legs, head, color, length and density of curl hair, voice, habits. Number of marginal ray flowers in inflorescences golden rod (fam. Asteraceae) ranges from 5 to 8. The number of petals Anemone nemorosa (fam. Ranunculaceae) -6, and sometimes 7 and 8. The plants of one species or varieties differ from each other in terms of flowering, fruit ripening, and the degree of drought resistance. Thanks to the variability of individuals in a population is heterogeneous. Darwin distinguished between two basic forms of variation - non-hereditary and hereditary. Variability. Variability called general property organizmov acquire new features, differences between osobyami within sight. Variability of all the signs of organisms: the external and internal features of the structure, physiology, behavior, and others. Potomstve one pair of animals or plants grown from semyan one fetus, it is impossible to meet exactly the same individuals. In a herd of sheep of the same breed, each animal is different faint features: body size, long legs, head, color, length and density of curl hair, voice, habits. Number of marginal ray flowers in inflorescences golden rod (fam. Asteraceae) ranges from 5 to 8. Chislo petals Anemone nemorosa (fam. Ranunculaceae) -6, and sometimes 7 and 8. The plants of one species or variety from each several otlichayutsya other in terms of flowering, fruit ripening, and the degree of drought tolerance. Thanks variability osobey population is heterogeneous. Darwin distinguished between two basic forms of variation - non-hereditary and hereditary. Non-hereditary, or Modification, variation. It has long been observed that all the individuals of this species, varieties or species under the influence of certain causes of change in one direction. Cultivars in the absence of conditions under which they were derived person losing their money. For example, the cultivation of cabbage in hot countries do not form a head of cabbage. It is known that when a good fertilizer, irrigation, lighting plants shrubs and fruit abundantly. Horse breed, imported into the mountains or on the island, where the food is nutritious enough, eventually become stunted. Productivity of purebred animals in improved maintenance and care increases. All these changes are non-hereditary, and if the plants or animals to be moved to the initial conditions of existence, the symptoms return again to the original. Genetic variation. In addition, there is another form of modification variability - genetic variation that affects the chromosome or genes t. E. The material basis of heredity. Hereditary changes were well known to Darwin, he assigned them a greater role in evolution. Mutations can be minor and affect a variety of morphological and physiological characteristics of the organism, such as animals - size, color, fertility, milk and so on. N. Mutations can occur because of the wide variety of effects. Heredity and variation - different properties of organisms that cause similarity and dissimilarity with the parents and offspring with more distant ancestors. Heredity expresses the stability of organic forms in a number of generations, and variability - their ability to transform. Darwin repeatedly emphasized the need for the deep development of the laws of variation and heredity. Later they became the subject of study of genetics. Основная литература. 3. Яблоков А. В. Юсуфов А. Г. Эволюционное учение М., «Высшая школа», 2004 5.Иорданский Н.Н.основы теории эволюции. М,.1998 6.Варонцов Н.Н. Сухорукова Л.Н. Эволюция органического мира М.,1991 Дополнительные литературы. 9Билич ГЛ., Крыжановский В.А. Биология полный курс. Ботаника 2т.М., 2005 г. 10.Билич Г.Л.,Крыжановский В.А. Биология полный курс.Зоология. Зт. М.,2005 г. 11.Ильин А.Я. Философия и теория эволюции. М., 2004 г. 12.Шеппард Ф. Естественный отбор и наследственность. М., 2000 г.
Theme 12. Population - the basic unit of evolution. Ponyatie of the population. Main characteristics of the population as eco - Genetic system The concept of the population. Population - the smallest independent evolutionary structure. Species, subspecies, groups of several populations close naturally also possess intrinsic evolutionary fate, but they are not basic (meaning indivisible) unit of life. In the evolutionary process is indivisible unit population, always serving as environmental, morphophysiological finally, most importantly, the genetic unity. Any changes to the individuals to any evolutionary processes themselves can not lead, individually and discretely changes occur yl g of the group to become exposed to those or other evolutionary factors, it is possible only within the population as a long-term, an organized group of individuals that group that indivisible without losing its integrity and other properties (and in this sense is elementary) and has its own evolutionary destiny. Main characteristics of the population as ekologogenetical system. Key environmental characteristics of the population - the value (in occupied space and the number of individuals), age and sex structure, and population dynamics Population range. Own space (area) is one of the important criteria for the population. Sure, as a part of the population has some type of habitat. Individuals outside of this area come from the population. Of course, the area of the population may grow, but for this population should learn this new space. This will only happen after turning it into a must for every ecological niche population. Space (area) occupied by the population can not be the same as for the different species and within species. For example, in a large mixed forest middle zone of the country, occupying more or less homogeneous areas of land in place can grow a small group of trees, no shrubs or perennial grasses, separated from other such groups of individuals of this species distance, the irresistible for pollen. The number of individuals in the population. Due to the size range of populations can vary considerably and the number of individuals in the populations. In insects, plants and small open spaces the number of individuals in some populations can reach hundreds of thousands and millions of individuals. On the other hand, animal and plant populations may be relatively small in number. Population dynamics. Population size (spatial and number of individuals) are subject to constant fluctuations. Causes of population dynamics in space and time are extremely diverse and in a general way to reduce the influence of biotic and abiotic factors. So, on one of the small islands near the coast of southwestern England lives in the wild population of rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). For the first time on a large number of oscillations of the evolutionary significance of individuals in populations noticed SS Bushels (1905), he called them the waves of life. These waves play the role of one of the factors of evolution, changing dramatically, and non-genetic composition of populations. The age structure of the population. The population consists of different age and sex of individuals. For each species, or even for each population within a species characteristic ratio their age group. These ratios affect overall survival, time to reach sexual maturity, intensity of reproduction - especially produced in the process of evolution as adaptation to specific conditions. Sex composition of the population. It is known that the genetic sex determination mechanism ensures cleavage offspring sex in the ratio of 1: 1 (primary sex ratio). Because of the unequal viability of male and female body is the primary relationship has sometimes markedly different from the secondary (typical at birth in mammals) and even more markedly different from the tertiary characteristic of adults. Knowledge of the ecological structure of the population (including the value of the population and its dynamics in space and time, age and sex composition and other characteristics of the individuals studied population ecology) - a must-depth study of populations as units of evolution in nature. Genetic heterogeneity of the population. SS Bushels (1926), based on the formula of Hardy, considered the real situation evolving in nature. Mutations usually occur and persist in the recessive state and do not violate the general appearance of the population; population saturated mutations "like a sponge with water." Genetic unity of the population. One of the most important findings of population genetics - the position of the genetic unity of the population, despite the heterogeneity of its constituent individuals (or perhaps precisely because of this heterogeneity), any population is a complex genetic system, which is in dynamic equilibrium. Population - the lowest number on the genetic system that can continue to exist for an indefinite number of generations. Population waves. Under natural conditions, periodic fluctuations in the number of different organisms are very common. In Figure 57 is shown as an example of changes in population size of predator and prey. We see that in different years, a sharp increase and decline in the numbers of animals, and changes in the number of the victim as to outstrip the number of predators. Chetverikov one of the first to draw attention to the periodic fluctuations in population size. Fluctuations in the number of individuals comprising the population are called population waves. Thus, the basic genetic characteristics of the population - a constant genetic heterogeneity, internal genetic unity and dynamic equilibrium of individual genotypes (alleles). These characteristics determine the organization of the Basic literature 2. Парамонов А. А. Дарвинизм. М. «Просвещение», 1999 3. Яблоков А. В. Юсуфов А. Г. Эволюционное учение М., «Высшая школа», 2004 Дополнительные литературы. 5.Иорданский Н.Н.Основы теории эволюции. М,.1998 6.Варонцов Н.Н. Сухорукова Л.Н. Эволюция органического мира М.,1991  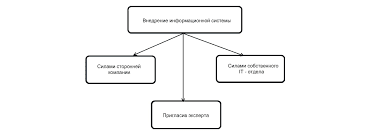 Что делает отдел по эксплуатации и сопровождению ИС? Отвечает за сохранность данных (расписания копирования, копирование и пр.)...  ЧТО ТАКОЕ УВЕРЕННОЕ ПОВЕДЕНИЕ В МЕЖЛИЧНОСТНЫХ ОТНОШЕНИЯХ? Исторически существует три основных модели различий, существующих между...  ЧТО И КАК ПИСАЛИ О МОДЕ В ЖУРНАЛАХ НАЧАЛА XX ВЕКА Первый номер журнала «Аполлон» за 1909 г. начинался, по сути, с программного заявления редакции журнала...  Что делать, если нет взаимности? А теперь спустимся с небес на землю. Приземлились? Продолжаем разговор... Не нашли то, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском гугл на сайте:
|