|
|
Topic-16. The emergence of adaptation - the result of natural selection1. Types of passive adaptation. 2. Complex adaptation 3. Physiological adaptation 4. The mechanism of adaptation 5. Classification of adaptations All curable during evolution features are certain adaptation (adaptation). This applies equally to the morphological characteristics of individuals, the formation of new populations and species change biogeocoenoses. The emergence of adaptation to the environment - the main result of evolution. Therefore, evolution can be seen as a process of adaptation of occurrence - adaptatsiogenez. Все закрепляющиеся в ходе эволюции особенности представляют собой те или иные адаптации (приспособления). Это в равной степени относится к морфологическим особенностям отдельных особей, образованию новых популяций и видов, изменению биогеоценозов. Возникновение приспособленности к среде — основной результат эволюции. Поэтому эволюцию можно рассматривать как процесс возникновения адаптации — адаптациогенез.
Thus, adaptation in the narrower sense - is the emergence and development of specific morphological and physiological properties, the value of which depends on those or other environmental conditions, ie. With. adaptation - it is always adapting to "something" and that "something" in the broadest sense - habitat. Means of passive protection. By means of passive protection, relative-syatsya such structures and features that only his presence with a greater chance of preserving life individuals in the struggle for existence. The animals often develop hard covers - a kind of protective shells of the type of education. Chitinous integument of arthropods. Achieved in a number of bugs and crustaceans exceptional hardness; solid shells of mollusks; bone cover reptiles, forming real shells in turtles, only a few examples of this kind. Rich in silica shell cells develop in many grains, calcium oxalate crystals are found inside cells REPAIRED-ryh plants; Both education are good protection against adverse conditions. Adaptive coloration - one of the most important passive protection of organisms. Without examining in detail all the variety of forms of adaptive coloration, give examples of patronizing and cautionary coloring and mimicry - imitative coloring and behavior. Protective coloration is often particularly important for the protection of organism in the early stages ontogeneza - eggs, larvae, juvenile and t. d. Thus, the eggs of birds, open gnezdyaschihsya in the grass or on the ground, always have pigmented shells corresponding to the color of the surrounding background. Interesting variety cryptic (hiding) is dismembered coloring coloring associated with alternating body of light and dark spots. For example, zebra and tiger poorly visible at a distance of 50-70 m, even in open areas because of the coincidence of bands on the body with alternating light and shadow in the surrounding countryside. Dismember coloring narushaet impression about the contours of the body. Cautions coloring. Very bright coloration is usually characteristic of the well-protected, poisonous, burning, Gilles and t. N. Forms. Bright coloration warns predators of advance inedibility object of their attack. The biological role of this painting has been well studied in the experiments. Individual "trial and error" in the end forced to abandon a predator attack on the victim with a bright color. Tackling contributed not only to the development of poisonous secrets, but the combination of them with a bright (usually red, yellow, black) color. Formation painting - the result of the interaction of elementary factors of evolution. Heritable changes in color of the body of individuals or bodies, initially random with respect to the background color, can in some circumstances bring success in reproduction. Even a partial coincidence coloring animals with the color of surrounding objects increases the chances of an individual in respect of leaving offspring. Mimicry. Interesting examples of adaptation comes from a study of imitation, mimicry (from the Greek. Mimikos- imitative) animals and plants, certain subjects inanimate and animate nature. Often imitation acts as a simple masking - Not only the protective coloring, but the mimetic similarity with any pre-Méthamis. For example, the caterpillar moth in resting position remarkably similar to a dry twig. Mimicry - similarity defenseless and edible species with one or more representatives are not genetically related species are well protected from predators. Sophisticated adaptation. In the development of evolutionary theory, special importance was the materialist explanation of the emergence of some very sophisticated adaptation by the accumulation of small hereditary deviations. Among these adaptations are considered below capacity for insectivorous plants, the development of the eye as an organ of vision, the occurrence of mutual adaptation in insects and flowering plants. Insectivorous and ability to move in plants. Predation for autotrophic organisms such as plants, is an exception, but nonetheless, even among hundreds of species of flowering plants are found carnivorous plants. Physiological adaptation. Numerous examples of physio-logical (functional) adaptation. For example, a plant known for complex physiological and biochemical mutations that led to the development of devices that are associated with the removal of the lack of oxygen: oxygen use photosynthesis, nitrate and organic acids as iCal-breathing material, switching pathways etc. D. The diverse and physiological mechanisms of adaptation plants and animals to a lack of water or extreme temperatures. Tackling all these cases contribute to the survival and reproduction of individuals preferential - enabling carriers of mutations in sootvetstvuyuschih conditions. The mechanism of occurrence of adaptation. In the broadest sense, adaptation means the harmony of organisms (including populations, species) with the environment. In the narrow sense, adaptation understand the special properties that can ensure the survival and reproduction of organisms in a particular environment. From this it is clear that adaptation is relative: adaptation to environmental factors one need not remain a fixture in other contexts. In an evolutionary sense, the concept of "adaptation" should refer not only to the individual animal, as to the populations and species. Changes within the same individual animal in response to certain environmental changes occur within the legacy of each singular reaction norm. Specific manifestations of the same adaptive responses during the ontogeny of the individual sometimes called acclimation, and changes in group I within the normal reaction of the form similar to groups of individuals - modifications. Literature 2. Парамонов А. А. Дарвинизм. М. «Просвещение», 1999 3. Яблоков А. В. Юсуфов А. Г. Эволюционное учение М., «Высшая школа», 2004 5.Иорданский Н.Н.Основы теории эволюции. М,.1998 6.Варонцов Н.Н. Сухорукова Л.Н. Эволюция органического мира М.,1991 Дополнительные литературы. 12.Шеппард Ф. Естественный отбор и наследственность. М., 2000 г   Что будет с Землей, если ось ее сместится на 6666 км? Что будет с Землей? - задался я вопросом... 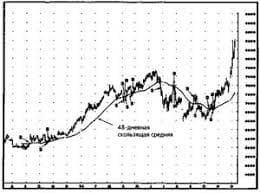 Что вызывает тренды на фондовых и товарных рынках Объяснение теории грузового поезда Первые 17 лет моих рыночных исследований сводились к попыткам вычислить, когда этот... 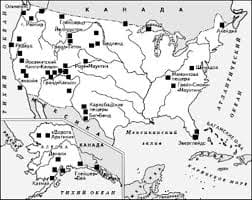 Система охраняемых территорий в США Изучение особо охраняемых природных территорий(ООПТ) США представляет особый интерес по многим причинам...  ЧТО ТАКОЕ УВЕРЕННОЕ ПОВЕДЕНИЕ В МЕЖЛИЧНОСТНЫХ ОТНОШЕНИЯХ? Исторически существует три основных модели различий, существующих между... Не нашли то, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском гугл на сайте:
|