|
|
Priorities of economic integration.⇐ ПредыдущаяСтр 16 из 16 International economic integration is peculiar to modern world economy. It represents process of economic, organizational and political association of the countries on the basis of a deep division of labour and steady interrelations between national economies, interaction of their economies on macro- and micro levels in the various forms. Among the forms of economic integration the following are allocated: the zones of free trade, within the framework of which the customs duties and other trade restrictions between the countries – participants are cancelled. The various international economic organizations have the special importance in expansion and deepening integration processes in world economy. Among them it is possible to allocate the General agreement on tariffs and trade (GATT) – regulate customs-tariff problems of world trade. Its successor is the World trade organization (WTO) conducting a line on liberalization of world trade by reduction of a level of the import duties, elimination of not tariff barriers etc. In the field of the money circulation and credit the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and International Bank of Reconstruction and Development (IBRR) work actively. The International Organization of Work works in the world market of a labour (solves the problems of employment, conditions of organization and payment of work, migration of a labour etc.) As the practice shows, internationalization of the economic relations is one of the fundamental laws of development of modern socially-historical progress.
AFTERWORD THE LITERATURE 1. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics. 6nd ed. 2011.- p.890 2. Mankiw, NG Principles of Economics. 2nd ed. / Trans. from English. - St. Peter, 2006.- p.624 3. Joseph E. Stiglitz, Carl E. Walsh. Economics. 4th ed./ W.W.W.Norton&com. New York/London. 2005.-p.971. 4. Hoag, Arleen J., 1944–.Introductory economics / Arleen J. Hoag, John H. Hoag. -- 4th ed. 5. Vdovina Е.К. An Introduction to International Economics. Part I. Введение в мировую экономику. (на английском языке). Part 1.: Teaching manual for students of specialty 080102 "World Economy". St Petersburg Polytechnic University, 2007, p.135. 6. Gerge Reisman. Capitalism. A treatise on Economics. Jameson Books, Inc. Ottawa, Illinois. 1998. p.1102 7. K.R.Makkonell Ekonomics: principles, problems and a policy. In 2 т. Т. 1: the textbook / K.R.Makkonell, s.l.brju.-: 2008. - p.467. 8. Dr. v. Loganathan. Economic theory. higher secondary - second year tamilnadu textbook corporation college road, chennai - 600 006. Government of tamilnadu. First edition – 2007 p.267. 9. P.H.Collin. Dictionary of Economics over 3000 terms. A&C Black Publishers LTD. Clearly definded Jul. 2006. p.225.
GLOSSARY A Absolute Advantage is the ability of a country to produce a larger quantity of a good with the same amount of resources as another country. Aggregate means the sum total. Aggregate Demand is the total demand for output by consumers, business, and government at each price level. Aggregate Supply is the total amount of output produced at each price level. Allocate means to distribute, as in the case of scarce resources or scarce goods. Antitrust legislation is aimed at reducing monopoly power. Assumptions are the simplifying device. Automatic Stabilizers, such as unemployment compensation and the progressive income tax structure, tend to move the level of income toward the full employment level and help “smooth out” the business cycle. Average Fixed Cost (AFC) is the total fixed cost divided by the number of units produced. Average-Marginal Relation specifies that if the marginal is greater than the average, the average will rise; and if the marginal is less than the average, the average will fall. Average Total Cost (ATC) is total cost divided by the level of output. ATC is found by the following expression: ATC average total cost total cost TC quantity of output Q Average Variable Cost (AVC) is the total variable cost divided by the level of output. The expression for AVC follows: AVC average variable cost total variable cost TVC quantity of output Q B Balance of Payments is the sum of the current account and the capital account from the international payments account. If this sum is positive, there is a surplus balance of payments, and if negative, a deficit. Balance of Trade is the difference in the value of what we export and what we import. If the value of what we import is greater than the value of what we export, then there is a balance-of-trade deficit. When the value of our exports exceeds the value of our imports, there is a balance-of-trade surplus. Balanced Budget results when tax collections and government spending are equal. Barriers to Entry are factors that keep firms from entering the market when there are incentives for them to enter. Barter System is a method of trade without money where one good is directly exchanged for another. Break-even Points are the points of intersection between demand and the average total cost. Any production level between the two break-even points yields an economic profit. Business Cycles are more-or-less-regular fluctuations in the level of economic activity. These are the up and down phases that accompany the increases or decreases in gross domestic product. Each business cycle goes through four phases: peak, recession, trough, and recovery. C Capital is a man-made tool of production; it is a good that has been produced for use in the production of other goods. Capital is a scarce resource. Capital Account is the international account that records the flow of money from one country to another for the purpose of buying financial assets. Capitalism is an economic system where the individuals own and control the resources. Cartel is a group of firms acting as one - in effect a monopoly -to determine the profit maximizing level of output and price. Change in Demand is a shift of the whole demand curve and occurs when a determinant of demand changes. Change in Quantity Demanded is a movement along the demand curve and occurs when the price of the good changes. Change in Quantity Supplied is a movement along the supply curve and occurs when the price of the good changes. Change in Supply is a shift of the whole supply curve and occurs when a determinant of supply changes. Circular Flow is a macro model showing the flows of income and product between consumers and business. Classical Economists believe that the economy will always achieve equilibrium at full employment. Communism is an economic system identified by public - government - ownership of resources. Comparative Advantage means a country can produce a good with a lower opportunity cost than the opportunity cost for the same good in another country. Complements are goods such that if you purchase more (less) of one, you purchase more (less) of the other. Conclusion is drawn from a model and is a prediction of behavior. Consumer Price Index (CPI) records the percentage change in the price of a selected number of consumer goods compared to a base year. Consumption (C) is the purchase of goods and services by households. Consumption Function is the direct relation between income and consumption that tells the amount of consumption at each level of income. Cost-Push Inflation is a rise in the average price level due to an increase in production costs. Cost-push originates from the supply side of the economy. Crowding-Out Effect occurs when deficit spending by government increases interest rates and reduces investment. Currency is the portion of our money supply consisting of coins and Federal Reserve notes. Current Account is the international account that essentially records the value of what is sold to foreign countries, the exports, minus the value of what is bought from other countries, the imports. Cyclical Unemployment occurs when the economy slows down and there are more unemployed people than there are available jobs. D Deficit Budget occurs when government spends more than it collects in taxes. Definition gives a name to an idea. Deflation is a continued fall in the price level and an increase in the value of a dollar. Demand is a list or schedule of the quantities of a particular good that a buyer would be willing and able to buy at alternative prices. Demand-Pull Inflation is a rise in the average price level caused by excess demand at full employment. The excess demand increases the average level of prices, which is inflation. Determinants of Demand, including a change in taste for a good, a change in income, an expectation of a change in the price of a good, or a change in the price of a related good, are capable of shifting the demand curve. Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand include whether the buyer views the good as a luxury or necessity, the availability of acceptable substitutes, and how large a part of the budget the purchase is for the buyer. Determinants of Supply are changes in nature, the cost of production, the price of other goods, and expectations of a change in price, all of which are capable of shifting the supply curve. Differentiated Product is one where the consumer can distinguish one firm’s output from another firm’s output. Discount Rate is the interest rate that banks pay on money borrowed from the Federal Reserve System. Disposable Income is income after taxes and can be either spent or saved by consumers. Disserving consumers are consuming more than they are making, either borrowing or spending past saving. Double Counting occurs when we count the value of the intermediate products as well as the value of the final product in GDP. E Easy Entry is the absence of entry barriers in a market. Easy entry results in more firms and less control over price; more barriers to entry result in fewer firms and more control over price. Economic Loss occurs when total cost exceeds total revenue. Economic Profit occurs when total revenue exceeds total cost. The revenue of the firm more than covers all opportunity cost. After paying the explicit cost and accounting for the implicit cost, the firm has revenue left over. This remaining revenue is economic profit. Economics is a social science that studies how society chooses to allocate its scarce resources, which have alternative uses, to provide goods and services for present and future consumption. Economic System is the process used by each society to allocate resources. Economies of Scale cause the average total cost to decline in the long run as the productive capacity of the firm increases and are a basis for natural monopoly. Efficient Allocation of Resources occurs when a good is produced at the lowest possible opportunity cost. This means as few of society’s scarce resources as possible are used up, leaving resources free to be used in the production of other goods. A firm produces efficiently at the level of output corresponding to the lowest point on the average total cost curve. Elastic Demand occurs if the coefficient of elasticity is greater than one. This means that buyers are relatively responsive to a change in the price of the good. Entrepreneurship is the organizational force that combines the other factors of production — land, labor, and capital — and transforms them into the desired output. Entrepreneurship is a scarce resource. Equation of Exchange says that the money supply times the velocity of circulation equals price times output, or MV = PQ. Equilibrium is a balance of forces. Equilibrium Point occurs at the intersection of the market supply and the market demand curves. Excess Reserves are any reserves that a bank has over and above its required reserves. A bank is free to make loans with its excess reserves. Exchange Rate is the price of one currency in terms of another. Expectations Inflation occurs when people expect prices to rise and act upon the expectation by buying more. Prices will rise as a result. Expenditure Approach to gross domestic product is the sum of all spending by consumers, business, government, and net exports. Explicit Costs are the money costs of producing the product. Externalities occur when the cost to society of production differs from the cost to the producer. F Fallacy of Composition is an error in thinking that assumes that the behavior of the whole is the same as the behavior of its parts. Fiscal Policy is the use of the federal budget as an economic tool to stabilize the economy. Fixed Factors of production are the inputs that cannot be increased during the short-run productive process. Fractional Reserve System requires that banks hold a percentage of their deposits as reserves. Free Good is a good with zero opportunity cost, which means that you can have all you want without giving up anything else. Frictional Unemployment includes those people in the process of relocating from one job to another. Full Employment is defined at some level of unemployment. The exact percentage of unemployment that marks full employment is open to debate. G GDP Price Deflator is a special price index used to convert money GDP into real GDP. Good is anything that satisfies a want. Government Spending (G) is the total expenditure by government. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total dollar value of all final goods and services produced within a nation’s border during a year. H Hyperinflation is an accelerating increase in the average price level. I Implicit Costs are the opportunity costs of owner-owned resources which are used in production, and for which no money is paid. Income is the money society earns through productive processes. The payments to resource owners are rent, wages, interest, and profit and are the returns to land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. Income Approach to GDP is found by adding all income received by the resource owners. Income Effect of a change in price measures the change in consumption of a good because of the change in purchasing power when the price changed. Income Multiplier means that any initial change in spending results in a greater change to total income. The income multiplier is the reciprocal of the marginal propensity to save. Inelastic Demand occurs if the coefficient of elasticity is less than one. This means that buyers are not so responsive to a change in the price of a good. Inferior Good is a good for which demand decreases as income increases. Inflation is a continued rise in the average level of prices. Investment (I) represents business spending for capital goods plus inventories. Business is the only sector of the economy that invests in the economic sense. K Keynesian Economists believe that the economy can be fine tuned using the fiscal and monetary tools. Kinked Demand is a model of oligopolistic behavior. L Labor is human effort, both physical and mental. Labor is a scarce resource. Labor Force consists of those employed and those unemployed but looking for work. Laissez-Faire is the classical attitude that the government should leave the macro economy alone. Land is land itself and anything that grows on it or can be taken from it – the “natural resources.” Land is a scarce resource. Law of Demand states that there is an inverse relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded of that good. Law of Diminishing Returns states that as an increasing amount of a variable factor is added to a fixed factor, the marginal product of the variable factor will eventually fall. Law of Increasing Costs states that as society obtains an extra unit of one good, ever-increasing amounts of the other good must be sacrificed. Law of Supply states that a direct relation exists between the price of a good and quantity supplied of that good. Long Run is a period of time in which all inputs to the productive process are variable. M Macroeconomics (macro) is the study of the economy as a whole. Marginal Cost (MC) is the change in total cost as one more unit of output is produced. It is the additional or extra cost of producing another unit. The expression for marginal cost follows: MC marginal cost change in total cost TC change in quantity of output Q Marginal Input Cost (MIC) is the change in total cost due to the hiring of another unit of a variable input. Marginal Product (MP) is the change in total product as one more unit of variable input is added to a productive process. Marginal Profit is the change in total profit when one more unit is produced and sold. Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) is the amount by which consumption changes when income changes by one dollar. The expression for MPC follows: MPC marginal propensity to consume change in consumption C change in income Y Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS) is the change in saving when income changes by one dollar. The expression for MPS follows: MPS marginal propensity to save change in saving S change in income Y Marginal Revenue (MR) is the change in total revenue as one more unit is produced and sold. Marginal revenue answers the question, What is the extra revenue from the sale of one more unit of output? The following is the expression for marginal revenue: MR marginal revenue change in total revenue TR change in output Q Marginal Revenue Product (MRP) is the change in total revenue due to the use of another unit of the variable input. Market is a situation where buyers and sellers meet to negotiate price and to trade. Market Power is the ability to control price. When a firm changes the price of its good, not only will it affect its own revenue, but it may affect the revenue of other firms as well. Market Structure refers to the elements of market organization that affect the behavior of the firms. Three elements identify the market structure: the number of firms in the market, freedom of entry and exit, and the degree to which the product is standardized. Measure of Debt is a function of money that records the amount of money to be paid in the future. Medium of Exchange is anything that is generally accepted in exchange for goods and services. Medium of exchange is a function of money. Microeconomics (micro) is the study of the individual parts of the economy. Misallocation of Resources occurs when a good is produced at other than the lowest point on the average total cost curve. Model is a simplification of reality. Monetarists believe only changes in the money supply affect output or prices. Monetary Policy is the use of monetary tools by the Federal Reserve System to influence the money supply and interest rates to stabilize the business cycle. Money serves as a medium of exchange and also functions as a standard of value, a store of value, and a measure of debt. Anything that is money performs these functions in a society. Money or Current GDP is the GDP figure without adjustment for changes in price. Money Demand tells how much money people will hold in currency or in checkable deposits at each interest rate. Money Multiplier is the multiple change in the total money supply resulting from any initial change in bank excess reserves. The money multiplier is the reciprocal of the reserve requirement. Money Supply in the narrow M1 definition consists of currency in circulation and any checkable deposits. Monopolistic Competition is characterized by a market structure that has many sellers, a differentiated product, and easy entry. Monopoly is a market structure where there is a single seller, no acceptable substitutes for the product, and entry into the market is restricted. The firm faces the same downward-sloping demand as the market because the firm is the market. N National Debt is the outstanding government debt created when the government spends more than it collects in taxes. The national debt is also commonly referred to as the federal or public debt. Natural Monopoly is characterized by a market that is large enough to support only one firm of an efficient size. Natural Rate of Unemployment is frictional plus structural unemployment. Net Exports is the difference between exports and imports and accounts for the foreign sector in the expenditure approach to GDP. Normal Good is a good for which demand increases as income increases. Normal Profit results when total revenue equals total cost. A normal profit is also called a zero economic profit. This means that the firm exactly covers its opportunity cost. Normative models express value judgments that prescribe how the world should be. O Official Settlements Account is the international account that includes the movements of cash from one country to another or the movement of credit from one central bank to another, and records changes in the government’s reserves of foreign currencies. Oligopoly is a market structure of just a few sellers, usually protected by barriers to entry, for a product that is either standardized or differentiated. Open Market is the exchange where negotiable government securities are traded, just like the stock market. Open Market Operation is the purchase or sale of negotiable government securities in the open market by the Federal Reserve. Opportunity Cost is the value of the foregone alternative — what you give up when you get something. P Per Capita GDP is GDP per person. To find per capita GDP, divide GDP by the population. Perfectly Competitive Market is a market structure characterized by many firms, a standardized product, and easy entry. When a market is competitive, no firm has control over price. Perfectly Elastic Demand occurs if the coefficient of elasticity is some number divided by zero. No matter how many units are bought, the price stays the same. Perfectly Inelastic Demand occurs if the coefficient of elasticity is zero. No matter what the change in price, the quantity demanded does not respond. Phillips Curve shows the inverse relation between unemployment and inflation. The outward shift of the Phillips curve shows stagflation. Positive economic models are models that describe. Potential Equilibria are the combinations of Y and C + I (or C + I + G) where equilibrium could possibly occur, where Y = C + I (or Y = C + I + G). Price is what the buyer gives up to get another unit of a good. Price Elasticity of Demand measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to a change in price. Price Leadership is the practice of all oligopoly firms uniformly increasing price after an increase in price by the industry leader. The price leader may be the most powerful firm or simply one taking the position by custom. Producer Price Index (PPI) is a measure of the prices of certain goods sold at wholesale and is thought to be a predictor of consumer price movements. Production Possibilities model shows all possible combinations of two different outputs that the society is capable of producing. Profit is total revenue minus total cost. Profit Maximization means making the greatest possible amount of profit. Profit Maximization Point (input) is the point of intersection of the marginal input cost with the marginal revenue product. The level of input that this point represents is the profit maximizing level of input. Profit Maximization Point (output) is the point of intersection of the marginal cost with the marginal revenue. The level of output that this point represents is the profit maximizing level of output. Public Goods are goods that we consume collectively; that is, goods for which an increase in your consumption does not require me to decrease mine. Q Quantity Demanded is the amount a buyer is willing and able to buy at a specific price. Quantity Supplied tells the amount that a seller is willing and able to produce at a specific price. Quota is a restriction on the amount of a particular good that can be imported. R Rational Expectations is the belief that people adjust to expected actions by the government so that, when the action actually occurs, its effect has already been accounted for in the market. Real GDP is a measure of output produced by an economy valued in the prices of the base year. To find the real level of output, real GDP, divide the current level of output, money GDP, by the GDP price deflator index number for the current year: Required Reserves are the amount of its deposits that a bank is required to hold in reserve and not lend out. Reserve Requirement is the percentage of its deposits that a bank must keep in reserve as required by the Federal Reserve. Resources are the so-called factors of production or means of production. These resources can be classified as land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. S Saving (S) is that part of income that is not spent for consumption or taxes. Saving Function is the direct relation between income and saving that tells how much is saved at each level of income. Say’s Law states that supply creates its own demand. The meaning of this statement is that the money paid to resource owners for the use of their resources will be used to purchase the output of producers. Scarcity is the basic economic problem of unlimited wants competing for limited resources. Seasonal Unemployment occurs when workers are laid off during the off season. Shortage exists whenever the quantity demanded is larger than the quantity supplied at the going price. Short Run is a period of time in which at least one of the factors of production is fixed. Shutdown Decision tells the firm to stop production if its revenue does not cover its variable cost. Shutdown Point is the lowest point on the average variable cost curve. Socialism is an economic system that favors a combination of private and public ownership of resources. Social Science uses the scientific method to study human behavior. Stabilization Policy is any action taken by the government to smooth out the business cycle and includes both monetary and fiscal policies. Stagflation is undesirable rates of both unemployment and inflation together. An outward shift of the Phillips curve shows stagflation. Standard of Value is a function of money that permits people to measure and compare the values of different goods. Standardized Product is one where the consumer cannot distinguish one firm’s output from another firm’s output. The products seem identical. Store of Value is a function of money that allows people who have money now to spend it at a later time. Structural Unemployment occurs when there are many people unemployed while there are many jobs available, but the unemployed lack the necessary qualifications for the jobs. Substitutes are goods such that if you buy more (less) of one, you buy less (more) of the other. Substitution Effect of a change in price measures the change in consumption of a good because the good becomes a less or more attractive substitute for other goods. Supply is the list or schedule of alternative prices and the amount of the product that the seller is willing and able to offer for sale at each price. Supply-Shock Inflation is inflation that results from infrequent drastic changes in production cost of fundamental products. Supply-Side Economics is a view that emphasizes the importance of policy action on the aggregate supply curve. Surplus is the condition that occurs when the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded at the going price. Surplus Budget is a budget that results when the government collects more in taxes than it spends. T Tariffs are taxes imposed on imports. Technology is the knowledge required to turn inputs into output. Total Cost (TC) is the sum of the fixed cost and the variable cost at each level of output. Total Fixed Cost (TFC) is the cost that does not change with the level of output. This means that the total fixed cost remains the same, or constant, whether zero or an infinite amount of output is produced. Total fixed cost is not related to the level of production. Total Output is the amount produced by the economy, real GDP. Total Product (TP) is the total output produced by the inputs of a firm. Total Revenue (TR) is the money the firm collects by selling the good (price times quantity sold). Total Spending is the amount spent by all sectors of the economy, C + I + G (C + I in a two-sector economy). Total Variable Cost (TVC) are those costs that change with the level of output. U Underemployment occurs when workers can find only part-time employment or jobs not utilizing their skills. Unemployment exists when people are looking for a job, but they are unable to find work at the going wage. Unemployment Rate for the United States measures the percentage of the labor force who are not able to find employment. Unitary Elasticity means that the percentage change in quantity demanded will be the same as the percentage change in price. V Variable Factors of production, or variable inputs, are those inputs that can be increased during production. Velocity of Circulation is the number of times a dollar is spent in a year in buying the final output of the economy.
[1] С учётом реальной покупательной способности полученных доходов. Например, в 2011г. в Казахстане на 1665102 тенге или 11357 долл. США можно было купить столько товаров, сколько в США на 20668 долларов.  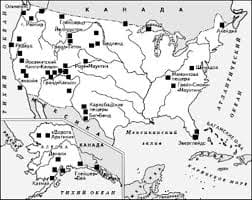 Система охраняемых территорий в США Изучение особо охраняемых природных территорий(ООПТ) США представляет особый интерес по многим причинам... 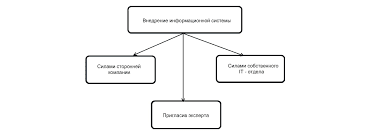 Что делает отдел по эксплуатации и сопровождению ИС? Отвечает за сохранность данных (расписания копирования, копирование и пр.)...  Что будет с Землей, если ось ее сместится на 6666 км? Что будет с Землей? - задался я вопросом...  Что делать, если нет взаимности? А теперь спустимся с небес на землю. Приземлились? Продолжаем разговор... Не нашли то, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском гугл на сайте:
|