|
|
To revise for an examination, revisionTo revise for an examination/test means "to go over the material on which one is to be examined/tested in preparation for the examination/test", and can generally be translated as подготовиться (к экзамену). e.g. a. (Teacher to class) — You must revise the izhole term's work for the exam. b. — You can revise either from your textbooks or from your notes.
revising. on (exam) revision. d. (Schoolchild/student to friend) — / can t go out tonight.
revise. do some revision. е. (Parent to child) — How are you getting on with your revision? To prepare (for an examination) is less often used in the sense of "готовиться (к экзамену)" and on the whole it is not to be recommended. However, it is possible to say, for example: — He came to the exam (completely) unprepared. To get ready (for an examination) suggests practical preparations just before an examination, for example, getting dressed, finding pens and pencils, and so on. To read (for an examination) is sometimes used in ccnnec-tion with a university degree. However, it does not mean ьре-cifically to revise for the degree examinations, but to follow the degree course, to study the subject (see unit 405).
e.g. a. — I'm reading for a history degree, history. This usage is rather formal, and becoming slightly old-fashioned. In cases where preparation consists entirely of reading books, mainly for the first time, it is possible to use read in the sense of "готовиться". However, such cases do not occur often. 338. to swot This is a slang word often used in connection with exams in the sense of revise, mainly in schools. e.g. — Richard's swotting for his exam. To swot may also be used like зубрить and a swot like зубрила. 339. to cheat (in an examination), to copy, to crib Cheat is a general word which covers all kinds of dishonest behaviour. In an examination context, however, it usually means having a book open under the desk, or using notes, or copying from someone else. In the latter case copy may be used. The two verbs occur in such sentences as:
a. Paul b. Ann copied from the girl next to her (in the exam) To crib is sometimes used in the sense of "to copy dishonestly". Hornby defines the verb as "copy (another pupil's written work) dishonestly". The noun crib is defined by Hornby as "word-for-word translation of a foreign text used by students of the language" and in the COD as: "translation for (esp. illegitimate) use of students". Cribs are printed booklets which were used by schoolchildren and students to avoid the necessity of translating the set books (see unit 219) for themselves. They held the crib under the desk, and, when asked to translate, read from the crib instead of giving their own translation. Or they used the crib in their preparation at home. Although cribs could be used at examinations, they seem to have been more often used at lessons. Nowadays such cribs are not widely used. There seems to be no special word in English for notes made for the purpose of cheating in an examination ("шпаргалка"). In some cases notes can be used. e.g. He took some notes into the exam. As no notes are allowed at most examinations, it is clear that the purpose was cheating. Otherwise the general word cheat can be used, as illustrated above. Types of Examination IN ENGLAND 340. In schools there are two types of examination: (1) school examinations These are set and marked by the staff of the school concerned, to assess the children's progress. They are sometimes held at the end of each term, but more often only once, at the end of the school year. If they are held at the end of term, they may be called end-of-term examinations. End-of-year examination is not common, however. Summer examinations is more often used in this sense. (2) public examinations These are set and marked by public examining boards. Those who pass these examinations are awarded certificates which are officially recognised as qualifications for entry to further and higher education, and for various jobs. They are: the General Certificate of Education, usually called the GCE. This was introduced in 1951, replacing the School Certificate. It is an academic type of examination, taken in two quite separate stages: Ordinary level ('0' level), usually taken at 15-16 Advanced level ('A' level), usually taken at 17-18 Places in higher educational establishments are awarded mainly on 'A' level results (see unit 120). the Certificate of Secondary Education, usually called the CSE. This was introduced in 1965 to cater for less academic pupils, who found the GCE too difficult, and either failed it or did not even take it, thus leaving school with no certificate of any kind. The CSE is usually taken at 15-16. A link between the CSE and GCE 'O' level is provided by the recognition of a grade 1 (see unit 356) in the CSE as equivalent to a pass at 'O' level. During the past few years various plans have been put forward for a unified system of public examinations for schools. One of these involves the introduction of a new examination, the Certificate of Extended Education (CEE), for those pupils who stay on at school after taking GCE 'O' level or CSE, but for whom 'A' level is too academic. Pilot examinations have been in existence for some years now, but in spite of widespread support for this examination from schools, the DES has still not come to a decision to recognise it. The latest proposals are for some kind of common examination at 16 + to replace the separate GCE 'O' level and CSE, with the GCE 'A' level remaining as it is (although possibly under another name, if 'O' level disappears). 341. In universities there are: (1) sessional examinations, often called simply sessionals. These examinations are held once a year, at the end of the session, or academic year (see unit 195), to assess the students' progress. The results do not affect their final qualification. If examinations are held in the middle of the session, they are called mid-sessional examinations or mid-sessionals. (2) final/degree examinations These are often called finals in non-formal style. They are longer examinations, very carefully set and conducted, and on the results of which degrees are awarded. Although most of the examiners are from the university concerned, there is also an external examiner, often called an outside examiner, from another university, to ensure objectivity. In the case of modern languages the traditional type of degree examination usually consists of 8-10 written papers of approximately three hours and an oral examination. 342. In colleges there are: (1) college/internal examinations, to assess the students' pro (2) public/external examinations, on the basis of which qual The Teacher's Certificate,  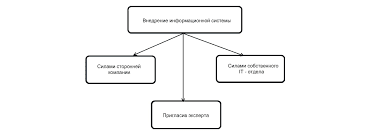 Что делает отдел по эксплуатации и сопровождению ИС? Отвечает за сохранность данных (расписания копирования, копирование и пр.)...  ЧТО И КАК ПИСАЛИ О МОДЕ В ЖУРНАЛАХ НАЧАЛА XX ВЕКА Первый номер журнала «Аполлон» за 1909 г. начинался, по сути, с программного заявления редакции журнала... 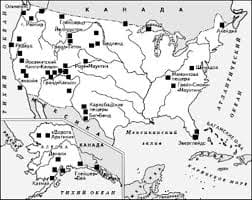 Система охраняемых территорий в США Изучение особо охраняемых природных территорий(ООПТ) США представляет особый интерес по многим причинам...  ЧТО ПРОИСХОДИТ, КОГДА МЫ ССОРИМСЯ Не понимая различий, существующих между мужчинами и женщинами, очень легко довести дело до ссоры... Не нашли то, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском гугл на сайте:
|