|
|
Lecture 14. Features a survey of children with disabilities.⇐ ПредыдущаяСтр 11 из 11 Objective: familiarization with the Features a survey of children with disabilities. Plan: 1. Features of Survey at PMPC 2. Requirements for experts Modern approaches to the education of children with disabilities are focused on the implementation of the special educational needs of each child, the maximum social integration of children with disabilities, the demand for professional and personal development. The methodological basis of psycho-pedagogical diagnosis of children with disabilities is the concept of systemic child's mental development, the theory of the unity of training and mental development, the theory of compensation of disturbed function in learning theory about the role of social environment in the development of the child and others. (LS Vygotsky, SL Rubinstein, PN Anokhin, Luria, VI et al.). The doctrine of the systematic development of the child's psyche allowed to form in the national scientific and methodological environment (VI Lubovsky, SJ Rubinstein, SD Zabramnaya, ON Usanova et al.) A comprehensive and systematic approach to the analysis of the mental processes the child in the process of examination by experts for psychological, medical and pedagogical commissions. A systematic approach to the examination of a child oriented professionals PMPC consider that every form of conscious activity, including training activities, is a complex functional system of the body and carried out by the joint work of all structures of the brain (block providing tone, regulation of activity and rest of the nervous activity unit ensuring receipt, storage and processing of information, block programming, implementation and monitoring activities, etc..). System approach implies to take into account the child's living conditions (social environment), the conditions of education and training (the quality of the educational environment), timeliness of care, and others. Thus, the PMPC specialists must carry out psychological and pedagogical diagnosis taking into account features and physiology of the nervous system of the child, the presence of hereditary factors and characteristics of the social environment, conditions and methods of education and training, age norms mental development of children and to make the conclusion, based on all the fundamental factors Considering the issues of effectiveness of the strategy and tactics of education of children with disabilities, the Commission should carry out the forecast for further development of the child in two ways: - Take into account the existence of conditions of the compensation system in an educational institution (or the possibility of its creation); - Take account of the absence of conditions for the organization of correctional and psychological and educational assistance to the child and the limited possibility of creating a psychological service. Therefore, every technician is required to carry out PMPC system diagnostics identity and level of psychological development of the child, to identify the causes of violations, to predict, justification for further education and development in the context of special psychological and educational support. An integrated approach to the examination of the child involves the interaction of specialists of different training, competent in the field of life of children and are responsible for their health, education and training (health workers, teachers, speech pathologists, educators, psychologists, social workers, etc.). Therefore, each PMPC expert must carry out system diagnostics identity and level of psychological development of the child within the framework of their competence, to identify the causes of disturbances in the development, behavior, adaptation in the children's collective, to predict, justification for further education and development in the context of special psychological and educational support. Systematic approach defines the tasks of psycho-pedagogical examination of children with disabilities. The main ones are: - Identify, qualify and secure features in the protocol of psychological development, emotional and volitional, behavior adversely affecting the training, communication and further development of the child; - To determine the nature of the violations, the structure and the degree of severity, have stored reveal features of mental development; - To determine the time factor disorders (whether stable or irreversible process is temporary); - To determine the approximate terms of compensation of violations in a special psychological and educational assistance (to take into account the pace of learning, forms of organization of the educational process, the scope, methods and forms of assistance); - Determine the most efficient type and form of further training. Academician VI Lubovsky formulate questions for experts to deliberate organization of examination of a child in the commission. In the limited time (2 hours - initial examination, 1 hour - again), you must identify: 1. Does your child have a violation of thinking, what is their structure and the degree of severity? 2. Does your child have a speech disorder, what is the structure and the degree of severity? 3. Violated whether learning, adaptation and communication modes of communication? 4. Does the speech violations are primary or secondary in nature? The last question has a methodological aspect and defines an important role in the Commission, a speech therapist teacher who, in accordance with professional competence should be shared with other professionals to determine the distinction between similar mental states (severe speech disorders and hearing loss, severe speech impairment and intelligence, serious violations of speech and vision, etc.). Methods of examination of children PMPC 1. Analysis of medical documentation (medical opinion on the state of vision, hearing, musculoskeletal system, physical and mental health, etc.). 2. Analysis of the OS documentation (specifications, products activity of the child, including test papers, drawings, opinions, speech therapy teacher and educational psychologist, etc.). 3. The method of conversation focused on the awareness of the child, his orientation in the environment, related to the inspection, others. 4. The observation method allows to form an opinion about the natural behavior of a child out of the situation and the survey during a training experiment (reaction to difficulties, the proposed aid, notes, promotion, etc.). 5. The method of teaching is a major experiment in the child's complex examination system and includes a set of techniques designed to study cognitive (including training), a child's activity. As part of the astronomical hours necessary to create conditions for the active work of the child under the supervision of the experimenter (teacher-speech therapist, educational psychologist, etc.). In carrying out examination of the child in the PMPC necessary to comply with the following requirements: - Verbal instructions are offered in accordance with the age and the level of the child's development of speech, sentence structure should be brief, clear pronunciation, intonation expressive. In severe disorders of speech instruction is carried out by means of non-verbal techniques and methods of presenting information; - Didactic material must be accessible, interesting, age-adequate and specific characteristics of the reception and processing of data of children with visual impairment, hearing loss, musculoskeletal system, speech and thought; - Tasks, including academic nature, it is necessary to offer in the form of a game, regardless of age (for students learning task must be motivated to change - evaluated not on the end result, and for the implementation of methods of action). The experimenter should strive to organize the interaction with the child, so that he can independently or with the help of an adult to disclose their potential development and training. This means that each job should include a system of methods and techniques that would allow the child to carry out their actions of analysis processes, synthesis, comparison, generalization, establishing causal relationships, the ability to plan and control their actions, actively demonstrate their attitude to the survey. During the survey it is necessary to encourage the child to receive care, to assess their learning difficulties and strive to overcome them, to create situations that encourage speech activity. In line with the objectives during the examination of the child in the PMPC leading Russian psychologists, speech pathologists, Methodists (S. Vygotsky, Luria, VI Lubovsky, SD Zabramnaya, SJ Rubinstein, A.. N. Usanova, etc.) is recommended to include a mandatory following methods: - Classification of objects or concepts; - Eliminate redundant object or concept; - Determination of the sequence of events, temporary or natural phenomena; - Determination of significant (main) characters, qualities, properties; - A simple analogy. During the examination of a child provisionally distinguish the following stages: 1. Introduction to survey the situation of the child The main purpose: to establish contact, message purpose of joint cooperation. To evaluate the nature of motivation, the presence or absence of contact, causes of possible failure of the communication. 2. Message instructions to the task Evaluated understanding of verbal instructions, the fullness of receiving information, the nature and availability of content. 3. Monitoring of the activities of the Child Evaluated on its own, and how to perform tasks, error correction capability, planning, monitoring, change of tactics, focus, commitment to results. 4. Implementation of aid Taking into account the amount (volume) and quality (forms, types and methods) help. According to leading experts in the field of special education and psychology (SD Zabramnaya, VI Lubovsky, ON Usanova et al.), Who in his works explore and justify the methods of psycho-pedagogical diagnosis of children with disabilities this parameter is important in assessing the child's rehabilitation potential. Working together with an adult child demonstrates its receptivity to learning, the ability to endure the manner shown in a separate action, the compensation methods ("zone of proximal development" in Vygotsky). Therefore every expert committee shall include training techniques mini-lessons. The experimenter should not only to draw up a set of procedures in accordance with the age and mental and physical characteristics of children, but also to articulate the instructions to tasks, to consider the scope, the sequence of presentation of information, methods and forms of assistance to each task. This approach allows us to show the visual aids to teachers, parents, the child himself is not only the difficulty of reception, processing and playback of educational information for children with disabilities, but also to justify the ways of compensating for these difficulties. 5. Evaluation of the results When analyzing the results of a survey of the child is important to consider the factors influencing the effectiveness of implementation of tasks: especially memory, concentration (attention), the regulation of their actions by voice control, orientation in the workplace, coordination of movements, especially fine motor skills. Every intelligent and practical action of the child must be considered from the standpoint of: - Forms of execution (mentally, with the help of visual aids, expanded instructions, display, etc.); - The degree of generality (collapse or expand the operation); - Degree of development (start-up phase of training, the level of automation and differentiation, etc.). In drawing up the final conclusion of the specialists commission must analyze and nature of the errors: - Whether they are systemic in nature (manifested in all activities) or random; - Whether there is fragmentation, the surface, distorted, incomplete perception of the information; - The conditions under which the number of errors increases (the length of time, the growing exhaustion of the nervous system, distracted by extraneous stimuli, etc.) - Under what types of assistance occurs error correction. At the end of the child's examination procedure is recommended to have an exchange of information between all experts agree on and generalize it, to formulate a final conclusion and recommendations. Meeting conducts Chairman, members of the Commission have to put a signature in the minutes of observation of the examination of the child and deliver their chairman. In case of dispute, to discuss results of the survey carried out without the presence of stakeholders (parents, representatives of the OU, etc.). At the end of the agreed joint decision of the commission, subject to the consent of the parents (legal representatives), the Secretary draws up the minutes, specialists can carry out individual consultations, explanations for parents (legal representatives), teachers, heads of DU on the organization of a special psychological and educational assistance. to professional training requirements A very important aspect of the quality of the psychological, medical and pedagogical work is not only the presence of the commission of specialists (speech therapists teachers, educators, psychologists, social workers, etc.), But in the first place - an adequate level of professional competence in related fields of scientific knowledge. Knowledge of the legal and regulatory framework, the essence of pedagogical, psychological, medical, social concepts necessary skill for close understanding in the Commission, the ability to navigate, negotiate and coordinate their conclusions and recommendations, with the main goal - implementation of protection of interests of the child with disabilities. Sufficient level requires a minimum of knowledge in the following disciplines: 1. Special (correctional) pedagogy 2. Special Psychology 3. Basics of psychopathology, child neurology, neurophysiology 4. Psycholinguistics 5. Psycho Special Education (preschool, on areas, educational levels of welfare activity) forms of knowledge about the organization and methods of teaching children with impaired speech, hearing, vision, intelligence). Special psychology gives the concept: - The general and specific regularities of mental development of children with disabilities; - Typological characteristics of children with delayed, Deficits, distorted or disharmonious development; - A complex defect structure (the relationship of primary and secondary disturbances in development); - The theory of compensation of disturbed functions, and others. Pathopsychology give an idea about the laws of decay of mental activity or the individual qualities of the person, on the distortion of brain (neural) activity on specific disorders of personality: perception, memory, thinking, mental health, etc. Neuropathology generates ideas about the structure of the nervous system, its functions (higher nervous activity), for neurological and psychiatric diseases and their impact on child development. Neuropathology reveals the concepts of the role of leading analyzers in the formation of the child's psyche: - On the structure and functions of the speech motor analyzer, a speech disorder caused by impairment of the central nervous system (alalia, aphasia, nasality, dysarthria) and their influence on the formation of speech and writing, adaptation, mental development of the child; - On the structure and function of the visual analyzer, its violations and the impact on mental development, training, adaptation of the child; - On the structure and functions of the auditory analyzer, its abuses and the effects of these disorders on learning, adaptation and mental development of the child. Psycho diagnostics forming methods of examination of children with disabilities, the knowledge of the method of study of higher mental functions, interpretation of the results.
Lecture 15. Clinical examination methods: survey; examination of the child; anthropometry; palpation. Clinical and genealogical research method. Laboratory testing methods. Instrumental methods of research.
Objective: to give information about the clinical examination methods Plan: 1. Clinical examination methods: survey; examination of the child; anthropometry; palpation. 2. Clinical and genealogical research method. 3. Laboratory testing methods. 4. Instrumental methods of research.
Diagnostics - a key step in the treatment of any disease. From fidelity and accuracy of the diagnosis depends on further treatment strategy. All the diagnostic methods of examination can be divided into two categories: • Clinical methods - are held directly by your doctor. • Additional (or paraclinical) - carried out by a physician using specific diagnostic methods. patient diagnosis is established on the basis of clinical and paraclinical studies. Clinical methods of examination include history taking, examination of the patient, palpation, percussion and auscultation. anamnesis History - is information about the history of the patient's disease, which is obtained by questioning the patient and / or his loved ones. In certain situations the doctor may need medical history and / or history of the patient's life. History of the disease - a collection of information about the beginning and course of the disease. When collecting medical history doctor discovers the nature of the patient's complaints and their change over time. A short history usually indicates the presence of an acute illness and anamnesis lasting usually indicates chronic pathologic process. Life history - is to collect data on the physical, mental and social status of the patient throughout his life. History taking in patients with mental disorders provides for subjective (from the patient) and objective information, which can be obtained from the patient's friends. PATIENT EXAMINATION There are general and special inspection. General inspection carried out in all cases, regardless of the patient's complaints. Special inspection is carried out by specialists (eg, gynecologist, urologist, ophthalmologist) using the special tools. On examination, the patient's condition is assessed overall, his body position, posture, facial expression, skin color, height, weight, gait. We examine the head, face, neck, trunk, limbs, genitals, assessed the state of the adipose tissue, bones, muscular system and lymph nodes. PALPATION Palpation - tactile method of study patients. With palpation is possible to determine the place of the location of their consistency, the nature of mobility, flexibility, local temperature. Also, in some cases, palpation reveals abnormal formation in the various cavities of the body. Palpation is superficial and deep. The latter is carried out only after the superficial palpation. In carrying out systematic surveys conducted palpation of the skin, muscles, bones, chest, abdomen and lymph nodes. In the study of the internal organs can be used special palpation techniques: transrectal palpation of the pelvic organs, kidneys bimanual palpation, vaginal palpation of the uterus and others. PERCUSSION Percussion - survey method based on the rapping parts of the body and further interpretation of the sound produced during the examination. Percussion is often used in cases of suspected presence of compacted fabrics, definitions Hollow, flexibility and lightness of tissues and organs. AUSCULTATION Auscultation - the method of clinical diagnosis, which is based on listening and further interpretation of the sounds that are produced by the various bodies. There are direct and indirect auscultation. Direct auscultation involves attachment doctor ear to the patient's body surface. Indirect auscultation - is the use of special tools that enhance the sound. Normal operation of the internal organs is characterized by certain sounds, and the development of pathological process is changing the nature of sounds that allows the physician to suspect the presence of diseases. The data from all clinical diagnostic methods allow the doctor to identify the proper benchmark in the way of diagnosis. If necessary, the doctor refers the patient to carry out further special examination methods. Clinico-genealogical method One of the prerequisites the correct and timely diagnosis, prevention and treatment of hereditary diseases, as well as the determination of genetic risk and clinical prognosis for the patient's relatives is the use of clinical-genealogical method. For the first time this method has been introduced in medicine F. Galton in the last century. In our country, the most complete and widely pedigrees analysis method applied in clinical practice excellent clinician, geneticist and neurologist, Professor SN Davidenkov. Clinico-genealogical method is based on an analysis of the nature of transmission of various symptoms and diseases in a single family with an indication of kinship between members of the pedigree. Clinico-genealogical method helps to make a correct diagnosis and therefore to choose adequate treatment and time to carry out targeted preventive measures. Therefore, going to the doctor-genetics, the couple should be well prepared. It is necessary to ascertain the state of health or the cause of death of the nearest and distant relatives from both the wife and by the husband. It is desirable to know not only the maiden names of women pedigree, but also age, and even better - the date, place of birth and residence of their ancestors. For families the parents of the patient, or just the consulted person in a geographically isolated area in closely spaced areas suggesting a common ancestor, which may contribute to the accumulation of more of the same genes, helps to identify the presence of the family of consanguineous marriages. Marriages between close relatives increases the risk and are of great importance when considering diseases with hereditary predisposition. In addition, the doctor-genetics should be told about the ethnic origin of the family, for persons of different ethnic groups (eg, Jews, Uzbeks, Finns and others.) Have increased susceptibility to certain hereditary diseases. Correctly and accurately collected data gives the doctor information and often serve as the basis for the diagnosis of hereditary diseases. It is known saying: "How many families, so many secrets." Practical experience proves that often families are hiding the facts of diseases, providing false information about fatherhood and so on. N. Pedigree is based on a sense of trust relationship to the doctor, cross-comparison of data surveys and inspections relatives. Therefore, you should not be surprised if the doctor-geneticist (after mandatory consultation with Consult) invite for an interview and clinical examination of his relatives, assigning them additional clinical and instrumental examination, ask to provide for the study of photographs of family members, if necessary - medical documents confirming or absence of a disease. It should be understood that this is done only in the interests of the consulting! After all, only in the case of reliably collected pedigree specialist can determine the type of inheritance of the disease and thereby confirm the diagnosis, identify those in need of medical and genetic counseling, to determine the clinical prognosis for the patient and his relatives, and to develop a plan of treatment, rehabilitation and prevention, taking into account individual and family characteristics of the disease. Each family is pedigree, which are used for certain symbols. Graphical representation of the pedigree is accompanied by "legend" (information), which highlighted the details of each family member and symbols used in the scheme. After anamnesis and graphic pedigree conducted clinical and genealogical analysis, which allows to determine the hereditary nature of the disease, the type of his inheritance, the outlook for posterity, to find out who the members of the pedigree of the most threatened in terms of the appearance of the same pathology. Appoint additional diagnostic measures necessary to complete consultations determined prognosis of the disease and its possible complications, selected the optimal therapeutic measures. The use of clinical-genealogical method involves along with the collection of family history thorough clinical, laboratory and instrumental examination as possible of all family members. Clinico-genealogical (genealogical) method is based on data obtained from the proband and his family members during the initial appointment with a doctor. This method is an integral part of the initial reception. Genealogical method refers to the oldest methods of medicine, but still is and will remain one of the most sought after. This method is relatively simple and available. Its essence is to collect physician genealogical data necessary for the subsequent compilation and analysis of the proband's family pedigree. The collection of such data is aimed at identifying and studying the symptoms of hereditary and congenital disease that appeared in the proband and his patients and healthy relatives. The procedure for collection of genealogical data and the nature of the questions asked of the proband and his close relatives are given below. During data collection, it is desirable to use family photo albums, medical records and other documentation. In drawing up the pedigree doctor uses standard techniques and symbols. The individual, which begins with genealogical research, - a proband. Brothers and sisters of the proband - a proband siblings (family, cousins, second cousins). Each person included in the family lineage, gets its symbol (square stands a man, a circle - a woman), and cipher, consisting of two digits (Roman denotes the generation number in the pedigree Arabic - an individual number in the pedigree, the numbering of the members of one generation is performed sequentially from left to right). There are other symbols (symbols): abortion, heterozygous carriers of the mutant gene, mono- and dizygotic twins, miscarriage (spontaneous abortion), one dead, the deceased individual, etc. Under the family lineage placed her legend decryption conventionally accepted designation. Schematic representation of a family tree begins with the proband (marked by arrow), which is usually located in the latter (under study) family generation. Family pedigree should cover at least two to three generations of relatives. Limitations in the number of analyzed generations there, and the more they investigated, the more reliable are the conclusions.
Next collected and designated data on children of the proband (if an adult) and his sibs (including a sequence of pregnancies and their outcomes). Then, gather information about relatives on the mother's side, first of all proband mother, her siblings and their children, and then all of my grandmother on the mother, her siblings and their children and grandchildren. If possible, gather information about the great-grandmother of the proband. In the same sequence gather information about relatives on the father. The next step - an analysis of the causes of an existing disease (trait). There are crucial: the value of the sample on which is made up pedigree (2-3 generations of relatives), the completeness of the registration carriers feature and other indicators. It must be remembered phenocopies disease. The current value of clinical-genealogical method can not be overestimated. The collected genealogical data doctor can determine the proband hereditary or non-hereditary nature of the disease (individual symptom), version of his inheritance (traditional monogenic or polygenic or non-traditional options), set in the case of monogenic variant localization of the abnormal gene on autosome or allosome (ie mapped gene), and to determine its frequency distribution in a population. Clinico-genealogical method was successfully applied to the analysis of coupling of the disease gene from his marker (marker locus). This analysis is widely used in the diagnosis of heterozygous states, prenatal diagnosis, early diagnosis of the disease in the preclinical phase, diagnosis and erased forms with late manifestation of the disease. For example, with the help of gene linkage analysis AIV diagnosed hemophilia, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Becker, myotonic dystrophy, hypoplasia syndrome Nail patella and the lack of many other diseases. After collecting genealogical data doctor starts an objective examination of the proband and his family members. Laboratory methods are widely used in clinical practice. We study the excretions and secretions, feces, blood, exudates and transudates. They are held in the following areas: 1) study of the general properties of the material, including physical (quantity, color, appearance, odor, nalichie impurities, relative density, and so on. D.) And the chemical study to determine prisutstviya of certain substances (substances normally contained in body fluids and substances which poyavlyayutsya only in diseases); 2) microscopic examination; 3) bacteriological and virological studies; 4) Serological diagnosis; 5) histology and cytology punctate bodies; 6) immunological studies. Actions of nursing staff in the preparation of patients for clinical and diagnostic laboratory tests. Instrumental study of the nervous system provide the most objective information about the presence of pathological changes, and are widely used in pediatric neurology. Craniography (x-ray of the skull). It is used to detect defects in the bones of the skull, a change in its internal relief of pathological calcifications in the brain (toxoplasmosis, hydatid disease, and others.) "Congenital malformations. X-ray is usually performed in two projections (face and profile). In the specialized neurological and neurosurgical departments are often used contrasting methods of brain and spinal cord radiography pneumoencephalography (PEG), ventrikulo-, myeloma and angiography. Transillumination (transillumination). It is used in the diagnosis of hydrocephalus, sub- and epidural hematomas. To conduct the study needed a light bulb of 100 watts, mounted in a special tube, easy-to-raying the bones of the skull. The study was conducted in a darkened room. With the penetration of the concentrated beam of light through the thin bone of the skull of the newborn baby or the first year of life in places where there is a pathological CSF glow (Fig. 28). Normally, around the glow tube in the form of the corolla in the frontal and parietal bones of the skull does not exceed 1.5-2 cm in the occipital bone, 1 cm. With the development of hydrocephalus glow can be spread around the skull. When sub- and epidural hemorrhages glow in no bruising. Echoencephalography. Based on the ability of intracranial structures having different acoustic impedance, partly reflects the direction of the ultrasound. Response ultrasonic vibrations are converted into electrical impulses that are registered on echoencephalography screen in the form of the curve. Using this method allows you to neurological, neurosurgical clinic to detect three-dimensional processes in the brain (tumor, bleeding, abscesses, hydrocephalic-hypertensive manifestations and others.). Signals comprising echo encephalogram normally include an initial complex, the median echo (M - echo) and the final complex. The most constant is the echo of the middle brain structures (III ventricle, the pineal gland, and others.), Usually located in the same place on the screen in the study encephalograph right and left. Electroencephalography. This registration of bioelectrical activity of the brain using a multichannel encephalograph, amplifying and recording biotoki brain. A study carried out in a specialized neurological department in the presence of shielded from the interference of light and a sound-proof chamber. To record encephalograms on the child's head, respectively, of the projection of the skull lobes applied electrodes which are lubricated with a special paste, which has a high electrical conductivity. The electrodes are usually fastened flexible helmet. During the study, the child should be in a calm relaxed state, because even the occasional muscle movements cause additional biotoki. Electroencephalogram (EEG) is a graphical representation of wave rhythms. In a healthy person at rest and wakefulness a-waves are detected at a frequency of 8-12 cycles per second and an amplitude of 40-70 mV and (3-waves with a frequency of 16-30 cycles per second and an amplitude of 10-30 mV. Rheoencephalography. This registration of changes electrical resistance of the brain by passing through AC high frequency and low power. The electrical resistance and the electrical conductivity of tissue depends on their blood supply, so the method rheoencephalography aims to study cerebral hemodynamics. When the expansion of the brain blood vessels and blood filling a significant electrical resistance decreases, and the narrowing of vessels - increases. Register of electrical resistance oscillations allows you to get an idea of the state of vascular tone, the size of their blood supply, the state of the walls of cerebral blood vessels. Normal rheogram is a regular wave like pulsovym. They distinguish the ascending portion and the descending part of the top. Normally, the apex slightly rounded. Rising part is seen as a-time (with 0,08-0,11) and characterizes the degree of elongation of the vascular wall. Downward part is defined as (3-time (0.5-0.8 s) and characterizes the elasticity of the vascular wall. The magnitude of the amplitude of the wave rheographic judge the severity of blood supply to the brain vessels. Rheoencephalography in combination with other methods helps identify conditions caused by cerebrovascular. Electromyography. This registration of bioelectrical activity of muscles using a cathode-ray oscilloscope or stub. Used to detect movement disorders and topical diagnosis of focal lesions of the nervous system. To avert the potential from the measured bioelectrical muscle, cutaneous electrodes apply a diameter of 0.5-1 cm. Metal plate electrodes with gauze pads soaked with saline, fixed on the skin bandages or rubber bands. The distance between them should be 1.5-2 cm. The registration is carried out at arbitrary contraction of muscles and tonic tension. EMG is a curve which takes into account the wave height, frequency, duration and waveform. Investigation of cerebrospinal fluid is often necessary for the diagnosis of meningitis, encephalitis, tumors, head injuries and other diseases. Spinal fluid obtained by lumbar puncture. In the specialized neurological and neurosurgical institutions sometimes resort to suboccipital and ventricular puncture. Lumbar puncture is usually performed in the treatment room or operating room, better on an empty stomach.
Lecture 16. The study of mental activity status
Objective: to give information about the clinical examination methods Plan: The study of mental retardation Current status of the study oligophrenics The study of mentally retarded children do not end examination in medical and educational commission. It continues in the institution where the child directs the Commission. The objectives of this study are different. Sometimes it is necessary to clarify the status of the child. This happens when a very complicated case in the differential-diagnostic attitude and one-time inspection in the Commission was insufficient. In conclusion, medical and pedagogical commission writes: "To send to a special school to provisionally re-examination in a year." These cases are rare, but they have a special responsibility on the teachers of the special school and require careful examination of the child. It must be from the first day at school to clarify the class, the group, in accordance with the general development of the child level, the extent of its knowledge and skills. A deep and comprehensive study is needed to improve the efficiency of the educational process. Knowing the individual characteristics of each child, the teacher has the opportunity to choose the appropriate methods, ways and means of corrective action. Systematic and focused study allows us to trace the dynamics of the development of children in a timely manner to find new areas of work with them, prognozirovatih state, make recommendations in the choice of profession, to maximize their social rehabilitation. In conducting the study should be guided by the same principles as in the examination of children in medical and pedagogical commissions: an integrated, comprehensive and holistic dynamic study of children taking into account their specific features. The stages of studying mentally retarded children The beginning of work with children preceded familiarize teachers with their personal affairs (medical and pedagogical documentation). Survey protocols in the commission provide the first information about the child, which allows teachers to correctly determine the child's place in the team, interested in his studies, to establish contact with him. It is important to take into account the state of hearing, sight, to immediately put his respective party. Materials characteristics reveal personality traits that should be considered already at the first contact with the child. If possible, it is necessary to speak in advance with the parents of the child. The next stage of the study puts special diagnostic purpose. In the context of supporting the schools, this work is carried out in the first two weeks of the school year. The program of studies includes "revealing lessons", which with the help of special assignments specified state of the mental processes of the child, compliance with this class. These experimental tasks are organically part of the learning process. Targeted studies of children, conductive under the special program, helps to identify certain aspects of the child's personality, which have not been seen by members of the commission at a short survey. After the first two "diagnostic" weeks beginning stage of the "current" study, which lasts the entire period of the child's stay in the institution. A very important issue is the design of the study materials the children. In the gardens, schools, children's homes for mentally retarded decided to keep a diary of observation. On the first pages of the diary written general information about the child's home address and parents' workplaces, data from the history of the development, diagnosis, garden figures, school, family (after the test conditions the teacher home education). All this information should always be on hand at teachers. Thereafter, the recording material begins the current study children. A mandatory requirement for keeping a diary is a regular records and analysis of observations. It is recorded, not all, but only the fact that increasingly characterizes the studied phenomenon, reflecting the progress in development of the child, or, conversely, indicates a deterioration of his condition. Entries must be precise and objective, fixed by the fact, rather than a generalized teacher's opinion of him. We can not postpone the recording. The blog made not only personal observations of the teacher, but also observing other teachers, technical staff, parents, children, and so on. N. In this case, be sure to note, from whose words made entry Very useful fix Entries (in those cases when it is necessary), and methods of teaching impact pupil reaction to that effect. Over the past decade, there have been new developments in the understanding of the essence of mental retardation, and to use the methods of its detection. This is primarily due to the success of science dealing with the problem. Clinical studies of the etiology and anatomical and physiological mechanisms of mental retardation, the latest hardware diagnostics, uphold the principles of determinism in medicine and psychology have contributed to the development of the most efficient ways and methods of selection of mentally retarded children in special institutions. Approve the personal approach when examining children with developmental disabilities. Now experts seek comprehensive, holistic, and more in-depth study of children, as well as early diagnosis of mental retardation. All big role to teaching, social environment. Materials XXIII International Conference, held in Geneva in 1960, show a variety of organizational forms of acquisition of special schools for children who are lagging behind in mental development. In most states, issues of selection involved not individuals (only teachers, or only doctors, or only psychologists), and the group of experts that make up the so-called commissions, teams, medical and psycho-social centers and other bodies, bearing different names in different countries. The data for some countries. In the United States (2d) selection of mentally retarded children is conducted by admission committees, which include doctors, school psychologists, speech pathologists, teachers, school nurses, specialists in hearing and speech, representatives of the school administration. Admissions Office along with a test of intelligence research conducts a psychological examination, which includes the study of speech development of the child, as well as the study of its emotional sphere and personal qualities. To this end, various questionnaires and projective techniques. Neurological examination to investigate the cause of existing difficulties and the child is determined by the method of treatment. The Commission summarizes the materials research and produces uniform way teaching remedial classes to the child. The main indicators of mental retardation consider the value of the intellectual coefficient (IQ) and social factor (SQ). Under SQ is the degree of sociability of the child, the ability to navigate. In the study of the IQ, t. E. The capacity for teaching, investigated the level of mastery in reading, numeracy, artistic development. For this purpose, various commonly used "batteries" tests. At the heart of most of the tests are tests Binet - Simon various upgrades. The most common scale Stanford - Binet and Wechsler scale for children. It should be noted that more and more demands are put multifaceted study of children with developmental disabilities and repeated surveys. In England (2d), there is the following order of selection. All children from the age of 5, are sent to regular schools. If within 1.5-2 years, they did not learn the program, the detailed characteristics of the teacher sent a neuropsychiatrist and a psychologist investigated. An indicator of underachievement believe that the child has not learned to count to 7 years. Psychologists examine the child with the help of tests. If children 6 years revealed clear signs of mental retardation, they are immediately sent to special schools. Thus, the mentally retarded, learning begins from 6-7 years. In England, as in the United States, extended the concept of mental retardation itself. It includes children educationally neglected, underdeveloped, with delayed mental and physical development, and so on. D. The main indicator of mental retardation is a value of 10. In this case, if the child lags behind their peers by 20%, then it is considered possible training in a special school or in special classes at public schools. If it falls short by more than 50%, then it is recognized and learning disabilities are placed in special boarding schools under the jurisdiction of the social security authorities. Many progressive oligophrenopedagogs psychologists and England oppose the test survey in determining the type of school believing that they check not only mental ability, as the general development associated with child rearing conditions, with the social environment and culture that surround it. It should be noted that the study of UK children are not only through the school, but in some cases, through special diagnostic centers. These centers are working on the delimitation of morons, imbeciles children from 6-8 years of age. The center may be 1-2 group (15-30 children), which are engaged from 6 months to 2 years. With a group engaged in the teacher and the assistant that allows deeply individualized work on the children. The children spend in group 6 hours (except classes have lunch and walk). During their stay in diagnostic centers, children learn the elements of reading and writing, as well as accurately identifies which of them can be trained at a special school, and who can not. In recent years, there is a tendency to early detection of mental retardation in children and timely transfer them to special schools. In France (2d) selection of mentally retarded children in special schools is carried out medical and pedagogical commission, which organizes all the work foremen school inspector. The committee also includes the director of the special school, teacher, doctor, psychologist. For the survey used Binet Tests - Simon Zaz- LP, Porteous. At the same time we have the tendency to study the qualitative uniqueness of children. In Norway (2d) the question of the transfer of the child to a special school is decided after long and careful research, which is attended by doctors, teachers, psychologists. In cases where the child's learning in regular school is unsuccessful and there are doubts about the mental faculties, it is placed for 3-4 weeks in a diagnostic band at a special school. The child are special observations. Psychologist along with psychometric tests conducts observations and experimental studies of perception, pro-cognitive processes, emotion, exploring the home environment, and so on. N. Then, these materials come to the children's neuropsychiatrist, and after the examination committee makes the final decision. In Denmark, Sweden, Netherlands much attention is paid to early diagnosis of mental retardation. The leading method of diagnosis of mental retardation there are psychometric tests. In Denmark (2d) have special preschool nurseries and kindergartens, which are diagnostic institutions. But since they are practically children with obvious mental retardation, further addressed the issue only on training opportunities in support of their schools or in the direction to deep backward home. The final decision on the direction makes a special committee, which includes a doctor, a teacher and a social worker to a special school. In Sweden (2d) in the selection of special schools also use tests. And advice for translation are sent to a special school children who unsuccessfully trained in a normal school. It should be considered as positive the fact that in Denmark and Sweden to the public schools there are special classes for "time studying" children with borderline states (among retarded and the norm). In these classes the children are special observations. In the Netherlands (2e) children diagnosed morons usually on the first years of teaching in public schools. After that, the child is sent to the Commission, which is conducting a survey and decide on the type of school. The committee consists of the director of a special school, a psychiatrist, psychologist and social worker. Psychometric tests are used for testing. Children imbeciles are diagnosed much earlier - in the preschool age and sent to special kindergartens. Of interest is the organization of assistance to mentally retarded children in Belgium. Special training and education of children in Belgium is continuing to 2.5 3 to 21 years; with 2.5-3 years old to 6 years of pre-school education, 6-8 years old to 13 years old primary school and from 13 years to 18-21 years - in high school. Identification in the development of children with disabilities held regional psychology of medical and social centers (PMS). Early diagnosis and care (from birth) implemented the centers of development and orientation. The main task of the PMS - advisory work with parents of children who have identified certain learning difficulties, behavior or deviations in psychophysical development. In the center, parents receive recommendations, where it is better to train the child. In the case of PMS need to forward it to the commission for transfer to a special school. The committee consists of physicians, psychologists, special education teachers, parents. The PMS state, along with these specialists are a physiotherapist, speech therapist, social worker, testers, assistant secretary. PMS gives an opinion on the feasibility of home schooling to those who can not learn in school. PMS conduct dynamic studies of children by testing for the entire period of study in their school. In all these and other countries, there has been a gradual abandonment of the use of intelligence tests as the sole method for the selection of children to school. Increasingly, the question of the revision of the theoretical foundations of testing, the need to rely on the psychological theory of mental development of the person. To approve the trend towards long-term study of children. Engaged in an intensive search for ways that provide more in-depth study of children. An important place is given to the survey by psychologists children. Great importance is attached to the definition of the forecast for each of the subject child. Note that in all these countries is carried out integrated teaching mentally retarded. The parents themselves choose the type of school for the child, but on condition that the help of experts. Of particular interest is the system of organization of examination of children in the eastern part of the Federal Republic of Germany (the former GDR), where there is a clear trend of a long and thorough study of the child. The project on the selection of mentally retarded children, developed by the Institute of Special Pedagogy still in 1952, highlighted the need for accurate diagnosis of the subject placed in a special group with special school, where for weeks by experienced teachers and a doctor must conduct lessons with children and to observe. In 1973 it issued a decree of the Minister of Education of the GDR on the selection of children in special schools. It also pointed out the need for mandatory weekly examinations of children, the status of which is below normal. During this week each qualifying child undergoes a medical and psychological examination. In group two pathologists usually work: one is a class, the other records the observations are transmitted to the medico-pedagogical commission. The medical and educational commission also received the conclusion of physicians, psychologists data, teacher characteristics. The following methods are used by the commission itself: observation, discussion, experimental psychological tasks. It should be noted that the Selection week and now considered mandatory for children in selecting them in special schools. Serious attention is paid early diagnosis of mental retardation. In some schools there is a special preparatory classes for children 6 years old. These classes perform kindergarten functions and at the same time are diagnostic. Long-term observations are complemented by psychological research. In some areas, practitioners follow the system of studying children. Before the start of the school year the school district offices hold meetings with the directors of auxiliary schools on the organization of admission of children to these schools. Directors of auxiliary schools are given the task to develop a training system to help mainstream schools to work with underachieving and "difficult" in the behavior of students, as its success will largely depend on how teachers in mainstream schools aware of the issues of mental retardation. Director mainstream schools for the new academic year should highlight the most experienced primary school teachers for special work on communication with the auxiliary school. These uchitelya- "communicators" are approved at the district school board.
 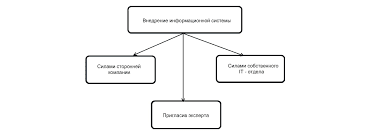 Что делает отдел по эксплуатации и сопровождению ИС? Отвечает за сохранность данных (расписания копирования, копирование и пр.)...  Конфликты в семейной жизни. Как это изменить? Редкий брак и взаимоотношения существуют без конфликтов и напряженности. Через это проходят все...  ЧТО ПРОИСХОДИТ, КОГДА МЫ ССОРИМСЯ Не понимая различий, существующих между мужчинами и женщинами, очень легко довести дело до ссоры...  Живите по правилу: МАЛО ЛИ ЧТО НА СВЕТЕ СУЩЕСТВУЕТ? Я неслучайно подчеркиваю, что место в голове ограничено, а информации вокруг много, и что ваше право... Не нашли то, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском гугл на сайте:
|