|
|
Faculty of law(s)/law facultyThis name requires no explanation. The plural form laws is still used in some universities because the original Latin name had the plural. The name of this faculty can be translated as юридический факультет. Faculty of social science(s)/social science faculty This is its usual name, although at Manchester and Leeds it is called the faculty of economic and social studies. It is combined with commerce at Birmingham and with law at Nottingham. Faculty of social science(s) can be translated as факультет общественных наук. Faculty of education/education faculty In a few universities this faculty is called the school of education, and in some others it is not a separate faculty, or school, but a department within the arts faculty. The main task of this faculty is to train graduates as teachers. Those who have taken a degree in one of the faculties already discussed, and who wish to become teachers, enter the faculty of education, either at the same university or a different one, and take a one-year teacher-training course (see unit 165). The name of this faculty can be translated as педагогический факультет. 88. These are the faculties which form part of all the civic 89. The administration of each faculty is the responsibility The dean is the head of the faculty. His deputy is usually known as the sub-dean, sometimes as the deputy dean. e.g. Dean of the Faculty of Arts/Arts Faculty (see unit 81) Sub-Dean of the Faculty of Science/Science Faculty Faculty board/board of the faculty This is the body which decides faculty matters. It consists of representatives from all departments of the faculty (see unit 91) and is presided over by the dean. A meeting of the faculty board is often called simply a faculty meeting in non-formal situations. e.g. a. There's a faculty meeting tomorrow at eleven. b. It was decided at the last faculty meeting. е. What's on the agenda of the faculty meeting? Note that sitting is not used in such cases (see unit 119). 91. Each faculty is divided into a number of departments. the Department of English/the English Department the Department of French/the French Department the Department of German/the German Department the Department of Classics/the Classics Department and so on (see unit 81). The word department can often be translated as кафедра. However, this is not an exact equivalent, because a department includes both staff and students. Here are some examples of usage. a. The Department of English is the largest in the faculty.
is on the staff of the b. Miss Glover English Department. teaches in the English Department.
е. (One student to another) — What department are you in? d. The department has decided to introduce a new course on the history of drama for the second year. Since both staff and students are members of the department, a meeting of the department or a departmental meeting could refer to both, but in practice it usually refers only to staff. To make this quite clear, staff meeting can be used. Head of department The person responsible for the running of the department is called the head of department. This term corresponds more or less to the Russian заведующий кафедрой. e.g. a. Professor Edwards is the head of the English Department. b. This application must be signed by your / the head of department. Secretary of the department/departmental secretary In English universities this is not one of the teaching staff who takes on administrative duties in addition to his/ her teaching, but one of the full-time administrative staff, with secretarial training, who deals with departmental correspondence, clerical work, and assists the head of department with routine administrative matters. Chair Chair means the position of professor, a professorship, and there may be one or more chairs in one department, depending on its size and importance. Here are some examples of usage. a. The chair of history at Exeter is held by Professor Thompson. b. The chair of English literature at Leeds has become vacant. c. Applications are invited for the chair of the Department of French. d. The university announced the creation of a new chair e. — I wonder who’ ll get the chair. Colloquial, meaning who will be appointed professor f. Professor Sanderson has been appointed to the new chair School In some English universities several related departments are grouped together in one school within the faculty. For example, the Leeds Science Faculty has the School of Chemistry, consisting of the departments of Inorganic Chemistry, Organic Chemistry, and Physical Chemistry, and the School of History, consisting of the departments of Ancient History, Medieval History and Modern History. Note, however, that this is not the only meaning of school in a university context. Some universities have schools instead of faculties (see unit 80). Other meanings are given in unit 414. External department London University has an external department, which gives people not studying at the university the opportunity of taking the degree examinations. Such people are called external students (as opposed to internal students) and take an external degree. The university does not provide any tuition for such students; they study for the examinations on their own, or take correspondence courses, or have private lessons. Extra-mural department An extra-mural department is one which runs non-degree courses in a wide range of subjects for the general public. As stated in the handbook for 1973/74 issued by the University of London Department of Extra-Mural Studies, the courses are for "adults who wish to pursue knowledge for its own sake or develop their talents more fully..." It continues "There are no entrance requirements apart from a willingness to take an active part in a serious course of study". The lectures take place on the university premises, and extra-mural is used here in a figurative sense, that is outside the main university framework (of degree courses and research), rather than outside its walls. The department has its own staff, and in addition arranges lectures by guest lecturers. Many universities have such departments. Non-University Institutions As already mentioned, the government and administration of non-university institutions differs from that of universities. The following terms are used: Governing body Instead of the court and the council, as in universities, colleges of education, colleges of higher education, polytechnics and other institutions of further education have a governing body, which consists of representatives of the local education authority, the local university, the college staff and the student body. Academic board This is responsible for the academic work of the college and its government, subject to the approval of the governing body. It thus fulfils approximately the same function as a university senate (see unit 74). Principal The head of a college or similar institution is usually called the principal. The principal is the effective head, not a public figure like the chancellor of a university. The princi-pal's deputy is called the vice-principal or the deputy principal. Director A comparatively new development is the use of director instead of principal in some institutions, especially polytechnics. This use is not very widespread at present but it is increasing. 102. Other administrative officers include the secretary, 103. The structure of colleges and polytechnics is on the whole simpler than that of universities. As a rule they have no faculties, but are divided only into departments. There is usually no need for departments to be grouped in faculties, because the range of subjects in a particular college is much narrower than in a university, and the subjects studied are usually related to each other. For example, in a college of technology mainly technical subjects are taught, and therefore in one respect the whole college corresponds to a single faculty of a university. If arts subjects are also taught, there may be an arts faculty and a science/technology faculty. In some large institutions there are schools, as in some universities (see unit 80) and some polytechnics have divisions. Many further educational institutions take not only full-time students but also part-time students. However, there are not usually separate full-time and part-time departments. Both full-time and part-time students study in the same departments, but take different courses, full-time courses or part-time courses. Most technical institutions also have so-called sandwich courses (see unit 396).  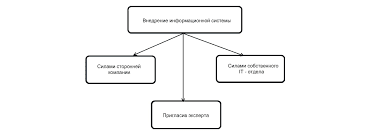 Что делает отдел по эксплуатации и сопровождению ИС? Отвечает за сохранность данных (расписания копирования, копирование и пр.)... 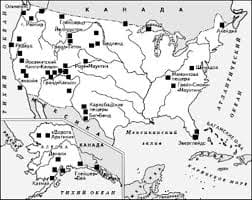 Система охраняемых территорий в США Изучение особо охраняемых природных территорий(ООПТ) США представляет особый интерес по многим причинам...  ЧТО ТАКОЕ УВЕРЕННОЕ ПОВЕДЕНИЕ В МЕЖЛИЧНОСТНЫХ ОТНОШЕНИЯХ? Исторически существует три основных модели различий, существующих между...  ЧТО ПРОИСХОДИТ, КОГДА МЫ ССОРИМСЯ Не понимая различий, существующих между мужчинами и женщинами, очень легко довести дело до ссоры... Не нашли то, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском гугл на сайте:
|