|
|
Глава шестая. Поменяйте свои привычки
1. Cheng et al. 2014. Prolonged fasting reduces IGF-1/PKA to promote hematopoieticstem-cell-based regeneration and reverse immunosuppression. Cell Stem Cell 14(6): 810–823. 2. Gersch et al. 2007. Fructose, but not dextrose, accelerates the progression of chronic kidney disease. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology 293(4): F1256–1261. 3. Jahren, A.H., and Kraft, R.A. 2008. Carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes in fast food: signatures of corn and confinement. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105(46): 17855–17860. Biello, D. 2008. That burger you’re eating is mostly corn. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/that-burger-youre-eating-is-mostly-corn/. Открыто 1 сентября 2016 г. 4. Bellows, S. 2008. The hair detective. https://uvamagazine.org/articles/the_hair_detective. Открыто 1 сентября 2016 г. 5. Gupta, S. 2007. If we are what we eat, Americans are corn and soy. https://www.cnn.com/2007/HEALTH/diet.fitness/09/22/kd.gupta.column/. Открыто 1 сентября 2016 г. 6. Brickett et al. 2007. The impact of nutrient density, feed form, and photoperiod on the walking ability and skeletal quality of broiler chickens. Poultry Science 86(10): 2117–2125. 7. Jakobsen et al. 2012. Is Escherichia coli urinary tract infection a zoonosis? Proof of direct link with production animals and meat. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 31(6): 1121–1129. 8. Gutleb et al. 2015. Detection of multiple mycotoxin occurrences in soy animal feed by traditional mycological identification combined with molecular species identification. Toxicology Reports 2: 275–279. 9. Piotrowska et al. 2013. Mycotoxins in cereal and soybean-based food and feed. In H.A. El-Shemy (Ed.), Soybean-Pest Resistance. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech. 10. Viggiano et al. 2016. Effects of an high-fat diet enriched in lard or in fish oil on the hypothalamic amp-activated protein kinase and inflammatory mediators. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 10: 150. 11. Aune et al. 2016. Nut consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer, all-cause and cause-specific mortality: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMC Medicine 14(1): 207. 12. Fontana et al. 2008. Long-term effects of calorie or protein restriction on serum IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 concentration in humans. Aging Cell 7(5): 681–687. Conn, C.S., and Qian, S.B. 2011. mTOR signaling in protein homeostasis: Less is more? Cell Cycle 10(12): 1940–1947. 13. Ananieva, E. 2015. Targeting amino acid metabolism in cancer growth and antitumor immune response. World Journal of Biological Chemistry 6(4): 281–289. 14. The Low Histamine Chef. 2015. Interview: Fasting mimicking diets for mast cell activation & allergies. https://thelowhistaminechef.com/interview-fasting-mimicking-diets-for-mast-cell-activation-allergies/. Открыто 1 сентября 2016 г. Глава седьмая. Фаза 1
1. Thompson, L. 2016. What does a three-day dietary cleanse do to your gut microbiome? https://americangut.org/what-does-a-three-day-dietary-cleanse-do-to-your-gut-microbiome/. Открыто 3 сентября 2016 г. 2. Angelakis et al. 2015. A Metagenomic investigation of the duodenal microbiota reveals links with obesity. PLos One 10(9): e0137784. Collins, F. 2013. New take on how gastric bypass cures diabetes. https://directorsblog.nih.gov/2013/07/30/new-take-on-how-gastric-bypass-cures-diabetes/. Открыто 3 сентября 2016 г. Глава восьмая. Фаза 2
1. University of California—Berkeley. 2016. Biologists home in on paleo gut for clues to our evolutionary history: Evolution of gut bacteria in humans and hominids parallels ape evolution. www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/07/160721151457.htm. Открыто 3 сентября 2016 г. 2. Walderhaug, M. 2012. Bad bug book, foodborne pathogenic microorganisms and natural toxins. Second Edition. K.A. Lampel (Ed.). Silver Spring, MD: U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2012. Pathogens causing US foodborne illnesses, hospitalizations, and deaths, 2000–2008. https://www.cdc.gov/foodborneburden/pdfs/pathogens-complete-list-04–12.pdf. Открыто 4 сентября 2016 г. 4. Bae, S., and Hong, Y.C. 2015. Exposure to bisphenol A from drinking canned beverages increases blood pressure: randomized crossover trial. Hypertension 65(2): 313–319. 5. Lebowitz, N. 2015. Nightshades & toxicity: Are “healthy” vegetables poisoning you? https://www.drnoahlebowitz.com/2015/01/02/nightshades/. Открыто 4 сентября 2016 г. 6. Parker et al. 1992. A new enzyme-linked lectin/mucin antibody sandwich assay (CAM 17.1/WGA) assessed in combination with CA 19–9 and peanut lectin binding assay for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Cancer 70(5): 1062–1068. Patel et al. 2002. Potato glycoalkaloids adversely affect intestinal permeability and aggravate inflammatory bowel disease. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases 8(5): 340–346. 7. Cordain, L. 2013. Are chia seeds permitted on the paleo diet? https://thepaleodiet.com/paleo-diet-special-report-chia-seeds/. Открыто 15 января 2017 г. 8. Kannan et al. 2003. Expression of peanut agglutinin-binding mucin-type glycoprotein in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma as a marker. Molecular Cancer 2: 38. 9. Wang et al. 1998. Identification of intact peanut lectin in peripheral venous blood. Lancet 352(9143): 1831–1832. 10. Singh et al. 2006. Peanut lectin stimulates proliferation of colon cancer cells by interaction with glycosylated CD44v6 isoforms and consequential activation of c-Met and MAPK: functional implications for disease-associated glycosylation changes. Glycobiology 16(7): 594–601. Gabius, H-J., and Gabius, S. (Eds.) 1996. Glycosciences: Status & perspectives. Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH. 11. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1983. Dermatitis associated with cashew nut consumption—Pennsylvania. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmw rhtml/00001269.htm. Открыто 4 сентября 2016 г. 12. Goodman, R. 2012. Ask a farmer: Does feeding corn harm c attle? https://agricultureproud.com/2012/09/27/ask-a-farmer-does-feeding-corn-harm-cattle/. Открыто 4 сентября 2016 г. 13. Rizzello et al. 2007. Highly efficient gluten degradation by lactobacilli and fungal proteases during food processing: New perspectives for celiac disease. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 73(14): 4499–4507. 14. Cuadrado et al. 2002. Effect of natural fermentation on the lectin of lentils measured by immunological methods. Food and Agricultural Immunology 14(1): 41–44. 15. Fontes, M. 2010. Are sprouted legumes paleo? https://thepaleodiet.com/paleo-diet-q-a-sprouted-legumes/#.VmNKHF876nM. Открыто 4 сентября 2016 г. 16. Buchmann et al. 2007. Dihydroxy-7-methoxy-1,4-benzoxazin-3-one (DIMBOA) and 2,4-dihydroxy-1,4-benzoxazin-3-one (DIBOA), two naturally occurring benzoxazinones contained in sprouts of Gramineae are potent aneugens in humande rived liver cells (HepG2). Cancer Letters 246(1–2): 290–299. 17. You, W., and Henneberg, M. 2016. Meat consumption providing a surplus energy in modern diet contributes to obesity prevalence: an ecological analysis. BMC Nutrition 2: 22. You, W., and Henneberg, M. 2016. Meat in modern diet, just as bad as sugar, correlates with worldwide obesity: an ecological analysis. Journal of Nutrition & Food Sciences 6: 517. 18. Fonteles et al. 2016. Rosemarinic acid prevents against memory deficits in ischemic mice. Behavioural Brain Research 297: 91–103. 19. Kim et al. 2016. Effects of linolenic acid supplementation in perilla oil on collagen-epinephrine closure time, activated partial thromboplastin time and Lp-PLA2 activity in non-diabetic and hypercholesterolaemic subjects. Journal of Functional Foods 23: 95–104. 20. de Lorgeril, M., and Salen, P. 2005. Dietary prevention of coronary heart disease: The Lyon diet heart study and after. World Review of Nutrition and Dietetics 95: 103–114. 21. Fahs et al. 2010. The effect of acute fish-oil supplementation on endothelial function and arterial stiffness following a high-fat meal. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism 35(3): 294–302. 22. Joelving, F. 2009. Lard lesson: Why fat lubricates your appetite. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/lard-lesson-why-fat-lubri/#. Открыто 11 декабря 2016 г. University of Michigan Health System. 2016. High-fiber diet keeps gut microbes from eating the colon’s lining, protects against infection, animal study shows. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/11/161117134626.htm. Открыто 11 декабря 2016 г. 23. Viggiano et al. 2016. Effects of an high-fat diet enriched in lard or in fish oil on the hypothalamic amp-activated protein kinase and inflammatory mediators. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 10: 150. 24. Bao et al. 2013. Association of nut consumption with total and cause-specific mortality. The New England Journal of Medicine 369: 2001–2011. Aune et al. 2016. Nut consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer, all-cause and cause-specific mortality: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMC Medicine 14(1): 207. 25. Chen et al. 2016. Resveratrol attenuates trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO)-induced atherosclerosis by regulating TMAO synthesis and bile acid metabolism via remodeling of the gut microbiota. mBio 7(2): e02210-e02215. 26. Pottala et al. 2014. Higher RBC EPA + DHA corresponds with larger total brain and hippocampal volumes: WHIMS-MRI study. Neurology 82(5): 435–442. 27. Hanley, D.A., and Davison, K.S. 2005. Vitamin D insufficiency in North America. The Journal of Nutrition 135(2): 332–337. 26. Cantorna et al. 2014. Vitamin D, immune regulation, the microbiota, and inflammatory bowel disease. Experimental Biology & Medicine 239(11): 1524–1530. Глава девятая. Фаза 3
1. Nichols, H. 2016. Worldwide obesity: Meat protein has as much effect as sugar. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/312080.php. Открыто 6 сентября 2016 г. You, W., and Henneberg, M. 2016. Meat consumption providing a surplus energy in modern diet contributes to obesity prevalence: an ecological analysis. BMC Nutrition 2: 22. You, W., and Henneberg, M. 2016. Meat in modern diet, just as bad as sugar, correlates with worldwide obesity: an ecological analysis. Journal of Nutrition & Food Sciences 6: 517. Vernaud et al. 2010. Meat consumption and prospective weight change in participants of the EPIC-PANACEA study. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 92(2): 398–407. 2. Pan et al. 2012. Red meat consumption and mortality: Results from 2 prospective cohort studies. Archives of Internal Medicine 172(7): 555–563. 3. Zamora-Ros et. al. “Mediterranean Diet and Non Enzymatic Antioxidant Capacity in the PREDIMED Study.” National Center for Biotechnology Information. U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2013. Web. 16 Feb. 2017. 4. Martínez-González et al. 2011. “Mediterranean diet and the incidence of cardiovascular disease: a Spanish cohort.” Nutrition, Metabolism, and Cardiovascular Diseases 21(4): 237–244. Martínez-González et al. 2011. “Low consumption of fruit and vegetables and risk of chronic disease.” Public Health Nutrition 14(12A): 2309-15. 5. Schünke et al. 1985. Lectin-binding in normal and fibrillated articular cartilage of human patellae. Virchows Archiv A Pathological Anatomy and Histopathology 407(2): 221–31. 6. National Institute on Aging. 2012. NIH study finds calorie restriction does not affect survival. https://www.nia.nih.gov/newsroom/2012/08/nih-study-finds-calorie-restriction-does-not-affect-survival. Открыто 6 сентября 2016 г. 7. Colman et al. 2014. Caloric restriction reduces age-related and all-cause mortality in rhesus monkeys. Nature Communications 5: 3557. 8. Fontana et al. 2008. Long-term effects of calorie or protein restriction on serum IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 concentration in humans. Aging Cell 7(5): 681–687. 9. Vitale et al. 2012. Low circulating IGF-I bioactivity is associated with human longevity: findings in centenarians’ offspring. Aging 4(9): 580–589. 10. Conn, C.S., and Qian, S.B. 2011. mTOR signaling in protein homeostasis: less is more? Cell Cycle 10(12): 1940–1947. 11. Orlich et al. 2013. Vegetarian dietary patterns and mortality in Adventist health study 2. JAMA International Medicine 173(13): 1230–1238. 12. Grant, W.B. 2016. Using multicountry ecological and observational studies to determine dietary risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 35(5): 476–489. 13. Drenick et al. 1972. Resistance to symptomatic insulin reactions after fasting. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 51(10): 2757–2762. 14. Owen, O.E. 2005. Ketone bodies as fuel for the brain during starvation. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education 33(4): 246–251. Cahill, G.F., Jr. 2006. Fuel metabolism in starvation. Annual Review of Nutrition 26: 1–22. 15. McClure et al. 2007. Abstract 3642: Fasting, a novel indicator of religiosity, may reduce the risk of coronary artery disease. Circulation 116: II_826-II_827. 16. Choi et al. A diet mimicking fasting promotes regeneration and reduces autoimmunity and Multiple Sclerosis symptoms. Cell Reports 5(10): 2136–2146. 17. Bhammar et al. 2012. Effects of fractionized and continuous exercise on 24-h ambulatory blood pressure. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 44(12): 2270–2276. 18. Obesity Society. 2016. Eating dinner early, or skipping it, may be effective in fighting body fat. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/11/161103091229.htm. Открыто 1 декабря 2016 г.  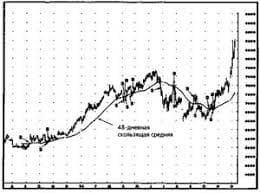 Что вызывает тренды на фондовых и товарных рынках Объяснение теории грузового поезда Первые 17 лет моих рыночных исследований сводились к попыткам вычислить, когда этот...  Живите по правилу: МАЛО ЛИ ЧТО НА СВЕТЕ СУЩЕСТВУЕТ? Я неслучайно подчеркиваю, что место в голове ограничено, а информации вокруг много, и что ваше право... 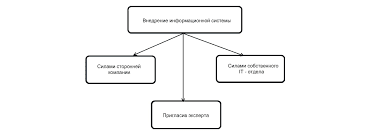 Что делает отдел по эксплуатации и сопровождению ИС? Отвечает за сохранность данных (расписания копирования, копирование и пр.)...  Что делать, если нет взаимности? А теперь спустимся с небес на землю. Приземлились? Продолжаем разговор... Не нашли то, что искали? Воспользуйтесь поиском гугл на сайте:
|